SHATAR VS SITTUYIN

SHATAR
Shatar (Mongolian: ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯ ᠰᠢᠲᠠᠷᠠ Monggol sitar-a, "Mongolian shatranj"; a.k.a. shatar) and hiashatar are two chess variants played in Mongolia. The rules are similar to standard chess; the differences being that: The noyan (ᠨᠣᠶᠠᠨ, lord) does not castle. The küü (ᠬᠦᠦ, pawn) does not have an initial double-step move option, except for the queen pawn or king pawn. In old shatar rules, a pawn that reaches its eighth rank must promote to half-power tiger. But a pawn could step back to its sixth rank to promote to all-power tiger. It moves like a queen. The baras (ᠪᠠᠷᠰ or ᠪᠠᠷᠠᠰ, tiger; Persian: fers) moves like a promoted rook in shogi: like a chess rook or one square diagonally. It was called half-power tiger or half-power lion in old shatar rules. In modern shatar rules, a baras moves like a queen. The mori (knight; ᠮᠣᠷᠢ) cannot deliver mate. In modern shatar rules, the mori can give mate. The bishop (teme) and rook (terge) move as they do in standard chess. The game always starts by White playing 1.d4 and Black responding with 1...d5. This is the only time in the game a pawn may advance two squares; some sources claim this initial move can optionally be made with the e-pawn. In old shatar rules, Ujimqin player must make an initial double-step move with the queen pawn; in Chahar, the king pawn. In old shatar rules, baremate is draw. In old shatar rules, one special rule is called tuuxəi, like komi in Go. A player could leave the enemy with only two pieces remaining (noyan and another piece) at the end. Then he must start making checks using the terge or baras and make consecutive checks until checkmate. Before checkmate, number of consecutive checks is the number of tuuxəi. If a player wins by checkmate as in chess, he receives only one tuuxəi. A player usually leaves the enemy with one noyan and one küü to allow time to put his pieces into good positions for making consecutive checks.
Statistics for this Xoptio
SITTUYIN
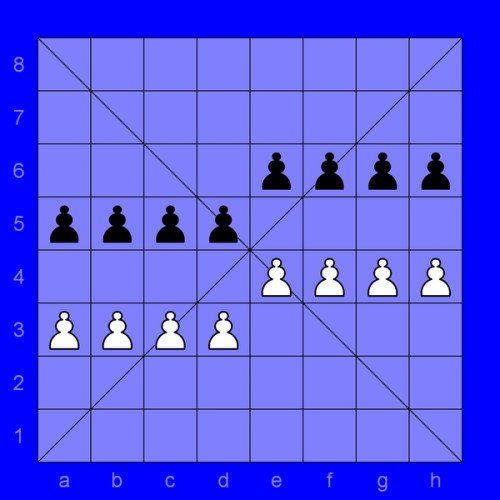
Sittuyin (Burmese: စစ်တုရင်), also known as Burmese chess, is a variant of chess that is a direct offspring of the Indian game of chaturanga which arrived in 8th century AD. Sit is the modern Burmese word for army or war ; the word sittuyin can be translated as representation of the four characteristics of army—chariot, elephant, cavalry and infantry. In its native land the game has been largely overshadowed by Western (international) chess, although it remains popular in the northwest regions. The sittuyin board consists of 64 squares, 8 rows and 8 columns, without alternating colors. It also consists of two diagonal lines across the board known as sit-ke-myin (general's lines). Only feudal lords (pawns) are on the board in the initial position. The game starts with the Red player (depicted here having white pieces), followed by the Black player, placing their other pieces arbitrarily on their own halves of the board (known as sit-tee or troops deployment): chariots can be put on any square on the back rank. In official tournaments, a small curtain is used on the middle of the board to prevent the players seeing each other's deployment during the sit-tee phase. One of the possible game openings is shown in the diagram. Feudal lords promote to general when they reach diagonal lines marked on the board. The promotion is possible only if that player's general has been captured. If the player has a feudal lord on a promotion square and his or her general is no longer on the board, the player can (if he or she wishes to) promote the feudal lord to general instead of making a move. A feudal lord which passes the promotion square cannot promote anymore.