OUK-KHMER VS XIANGQI
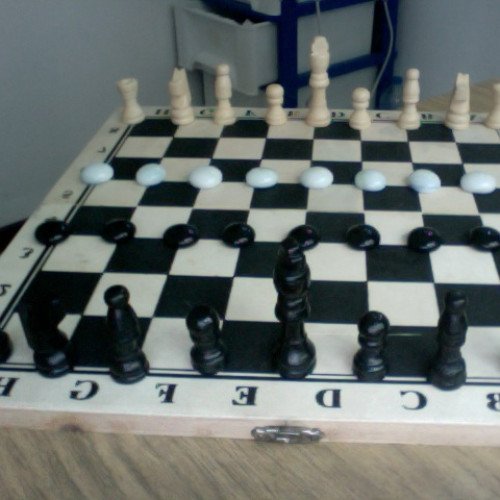

OUK-KHMER
Ouk-Khmer (also known as Cambodian Chess) is a chess variant which D. B. Pritchard claimed was played in Cambodia although its actual origins appear to be unknown. Pritchard gives the source as P. A. Hill. It combines elements of makruk and xiangqi. Similar to xiangqi, it is played on the intersections of an 8×8 monotone board (instead of 8×9). Contrary to Pritchard's claim, the actual variety of chess played in Cambodia today, known as "Ok" or "Ouk Chatrang", is nearly identical to makruk. The authenticity of the game described by Pritchard remains doubtful. Pritchard (The Encyclopedia of Chess Variants, 1994) described this game as "an old variant displaying elements of Burmese Chess, Chaturanga and Makruk". However, the rules provided appear to be a hybrid of Makruk and Xiangqi. For example, play on the intersections and the movement of the fish (pawn) follow Xiangqi rules. The advanced placement of the full line of pawns resembles the initial setup of makruk. The naming of the "boat" also follows makruk. John Gollon, the author of "Chess Variations: Ancient, Regional, and Modern", received a description of a chess game in 1969 from a U.S. serviceman who claimed to have obtained the details from a Cambodian born guerrilla officer he was questioning. The serviceman expressed concern that he may have been mistaken about some of the details and Gollon stated that he was never able to confirm the details with an official Cambodian source. He admitted in his letter: “The correspondent later expressed some concern that he may have been mistaken in some details.” In 2007, the English chess specialist John Beasley published a revised edition of late D.B.Pritchard's book (The Classified Encyclopedia of Chess Variants), in which more details from Gollon's letter were given (such as the local names of the chessmen, not included in the 1st edition) and where Beasley expressed his strong doubt about the authenticity of this kind of chess. In reaction to this publication, Beasley was sent information that a set of this chess had made an apparition in an exhibition in Tokyo in 2002 as well as in several Japanese books that preceded or followed, written by Umebayashi Isao and Okano Shin. They could have rediscovered these rules by translating a book bought in Cambodia, where the Elephant could not capture sideways. The names they gave for the chessmen were somewhat different from Gollon (Kwon, Neamahn, Kwo, Seh, Tuuk, Trey as for the table). Umebayashi and Okano designated that game as "shattrong". A photo of a complete set was available showing the 18 pieces on a board with marked diagonals. Beasley published a corrective note in the British specialized magazine Variant Chess (Issue 55, September 2007 and issue 64, August 2010 ) to acknowledge this second “evidence”. He acknowledged that the game is apparently absent "from the streets of Phnom Penh in 2003" and stated that Peter suggested "that this may have been a minor consequence of the mass killings of the Pol Pot era.". The situation has been cleared out in 2012 with the help of a Japanese chess researcher, Yasuji Shimuzu who got in touch with Umebayashi Isao. First, it has been now understood that Umebayashi and Okano's books were simply presenting a reconstruction of the “Cambodian” chess which they had discovered in Pritchard's first edition. As Pritchard didn't name the chessmen in his first edition, the Japanese authors extrapolated the names with the help of a dictionary. No Cambodian books had been consulted and even found. The difference in Elephant's move was simply a misreading. Finally, looking for an illustration, they just set up a set of makruk with additional Fishes and Officials over a facsimile Burmese board that they had and fitted well the size of his chessmen. John Beasley published a corrective note on his website http://www.jsbeasley.co.uk/. His conclusion is that the game described to P. A. Hill in 1969 appeared once more to reduce to a single informant whose statements were at variance with all other known testimony. Moreover, John Beasley has found and proven that the game is flawed if played seriously.
Statistics for this Xoptio
XIANGQI
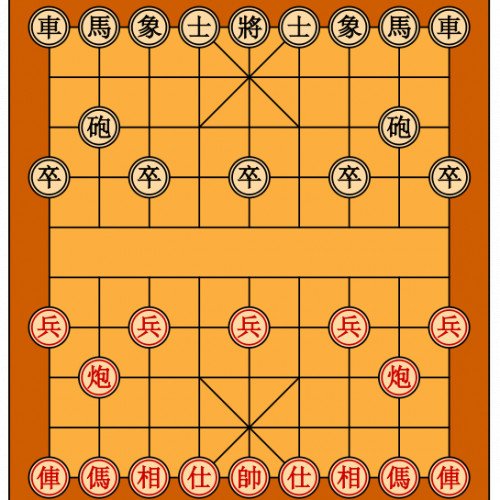
Xiangqi (Chinese: 象棋; pinyin: xiàngqí; Wade–Giles: Hsiang ch'i; English: /ˈʃɑːŋtʃi/), also called Chinese chess or Elephant chess, is a strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in China, and is in the same family as Western chess, chaturanga, shogi, Indian chess and janggi. Besides China and areas with significant ethnic Chinese communities, xiangqi is also a popular pastime in Vietnam, where it is known as cờ tướng. The game represents a battle between two armies, with the object of capturing the enemy's general (king). Distinctive features of xiangqi include the cannon (pao), which must jump to capture; a rule prohibiting the generals from facing each other directly; areas on the board called the river and palace, which restrict the movement of some pieces (but enhance that of others); and placement of the pieces on the intersections of the board lines, rather than within the squares. Xiangqi is played on a board nine lines wide and ten lines long. As in the game Go (圍碁; or Wei ch'i 圍棋), the pieces are placed on the intersections, which are known as points. The vertical lines are known as files (Chinese: 路; pinyin: lù; "road"), and the horizontal lines are known as ranks (Chinese: 線/綫; pinyin: xiàn; "line"). Centred at the first to third and eighth to tenth ranks of the board are two zones, each three points by three points, demarcated by two diagonal lines connecting opposite corners and intersecting at the centre point. Each of these areas is known as 宮 About this soundgōng, a castle. Dividing the two opposing sides, between the fifth and sixth ranks, is 河 hé, the "river". The river is often marked with the phrases 楚河 About this soundchǔ hé, meaning "River of the Chu ", and 漢界 About this soundhàn jiè, meaning "Border of the Han", a reference to the Chu–Han War. Although the river (or Hanchu boundary) provides a visual division between the two sides, only two pieces are affected by its presence: soldiers have an enhanced move after crossing the river, and elephants cannot cross it. The starting points of the soldiers and cannons are usually, but not always, marked with small crosses.