OPERATION VS SITTUYIN
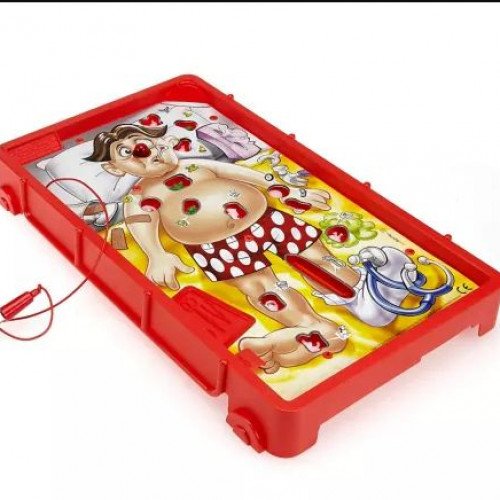

OPERATION
Operation is a battery-operated game of physical skill that tests players' hand-eye coordination and fine motor skills. The game's prototype was invented in 1964 by John Spinello, a University of Illinois industrial design student at the time, who sold his rights to the game to renowned toy designer Marvin Glass for a sum of US$500 and the promise of a job upon graduation (a promise that was not upheld). Initially produced by Milton Bradley in 1965, Operation is currently made by Hasbro, with an estimated franchise worth of US$40 million. The game is a variant on the old-fashioned electrified wire loop game popular at funfairs. It consists of an "operating table", lithographed with a comic likeness of a patient (nicknamed "Cavity Sam") with a large red lightbulb for his nose. This could be a reference to classic cartoons, where ill characters' noses turn red. In the surface are a number of openings, which reveal cavities filled with fictional and humorously named ailments made of plastic. The general gameplay requires players to remove these plastic ailments with a pair of tweezers without touching the edge of the cavity opening. Operation includes two sets of cards: The Specialist cards are dealt out evenly amongst the players at the beginning of the game. In the U.S and Australian version, players take turns picking Doctor cards, which offer a cash payment for removing each particular ailment, using a pair of tweezers (dubbed “Electro Probe” in earlier versions) connected with wire to the board. Successfully removing the ailment is rewarded according to the dollar amount shown on the card. However, if the tweezers touch the metal edge of the opening during the attempt (thereby closing a circuit), a buzzer sounds, Sam's nose lights up red, and the player loses the turn. The player holding the Specialist card for that piece then has a try, getting double the fee if he or she succeeds. Since there will be times when the player drawing a certain Doctor card also holds the matching Specialist card, that player can purposely botch the first attempt in order to attempt a second try for double value. The winner is the player who holds the most money after all the ailments are extracted. Subsequent later games removed the money and cards, and the winner of these editions is the player who removes the most ailments.
Statistics for this Xoptio
SITTUYIN
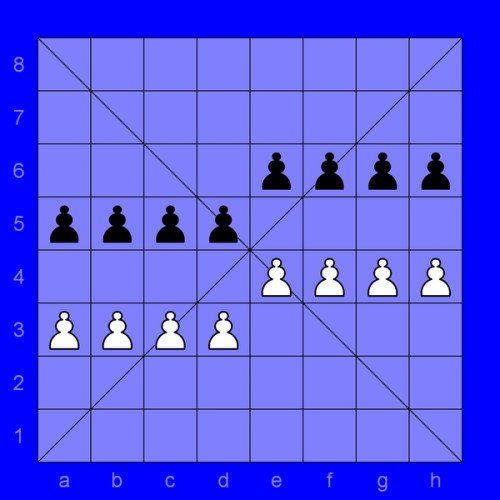
Sittuyin (Burmese: စစ်တုရင်), also known as Burmese chess, is a variant of chess that is a direct offspring of the Indian game of chaturanga which arrived in 8th century AD. Sit is the modern Burmese word for army or war ; the word sittuyin can be translated as representation of the four characteristics of army—chariot, elephant, cavalry and infantry. In its native land the game has been largely overshadowed by Western (international) chess, although it remains popular in the northwest regions. The sittuyin board consists of 64 squares, 8 rows and 8 columns, without alternating colors. It also consists of two diagonal lines across the board known as sit-ke-myin (general's lines). Only feudal lords (pawns) are on the board in the initial position. The game starts with the Red player (depicted here having white pieces), followed by the Black player, placing their other pieces arbitrarily on their own halves of the board (known as sit-tee or troops deployment): chariots can be put on any square on the back rank. In official tournaments, a small curtain is used on the middle of the board to prevent the players seeing each other's deployment during the sit-tee phase. One of the possible game openings is shown in the diagram. Feudal lords promote to general when they reach diagonal lines marked on the board. The promotion is possible only if that player's general has been captured. If the player has a feudal lord on a promotion square and his or her general is no longer on the board, the player can (if he or she wishes to) promote the feudal lord to general instead of making a move. A feudal lord which passes the promotion square cannot promote anymore.