MASTERMIND VS MATCHING GAME
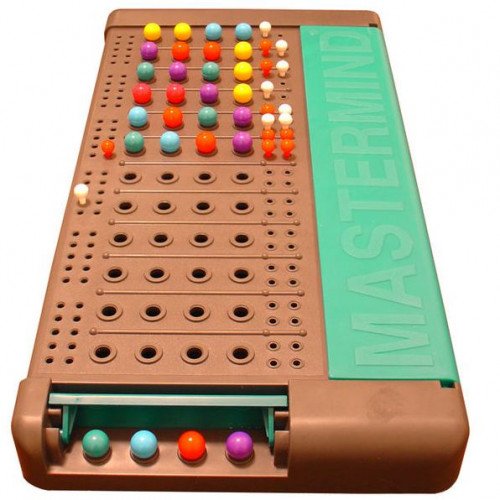

MASTERMIND
Mastermind or Master Mind is a code-breaking game for two players. The modern game with pegs was invented in 1970 by Mordecai Meirowitz, an Israeli postmaster and telecommunications expert.It resembles an earlier pencil and paper game called Bulls and Cows that may date back a century. The game is based on an older, paper based game called Bulls and Cows. A computer adaptation of it was run in the 1960s on Cambridge University’s Titan computer system, where it was called 'MOO'. This version was written by Frank King. There was also another version for the TSS/8 time sharing system, written by J.S. Felton and finally a version for the Multics system at MIT by Jerrold Grochow. The modern game with pegs was invented in 1970 by Mordecai Meirowitz, an Israeli postmaster and telecommunications expert. Meirowitz presented the idea to many major toy companies but, after showing it at the Nuremberg International Toy Fair, it was picked up by a plastics company, Invicta Plastics, based near Leicester, UK. Invicta purchased all the rights to the game and the founder, Edward Jones-Fenleigh, refined the game further. It was released in 1971–2. Since 1971, the rights to Mastermind have been held by Invicta Plastics. (Invicta always named the game Master Mind.) They originally manufactured it themselves, though they have since licensed its manufacture to Hasbro worldwide, with the exception of Pressman Toys and Orda Industries who have the manufacturing rights to the United States and Israel, respectively. Starting in 1973, the game box featured a photograph of a white man in a white jacket seated in the foreground, with a young Asian woman of high caste standing behind him with the golden symbols of office visible on her sari, denoting the power and intellect behind the throne. The two amateur models (Bill Woodward and Cecilia Fung) reunited in June 2003 to pose for another publicity photo.
Statistics for this Xoptio
MATCHING GAME
Matching games are games that require players to match similar elements. Participants need to find a match for a word, picture, or card. For example, students place 30 word cards; composed of 15 pairs, face down in random order. Each person turns over two cards at a time, with the goal of turning over a matching pair, by using their memory. Most matching games are objective, with correct answers in the rules for what counts as a match, pair, etc. Some however, like Dixit or Apples to Apples, are about subjective matches picked by one or more judge players. Here the correlation between a match holds value only as other players decide it, but rules dictate who will make those decisions and when.