LOST CITIES VS XIANGQI
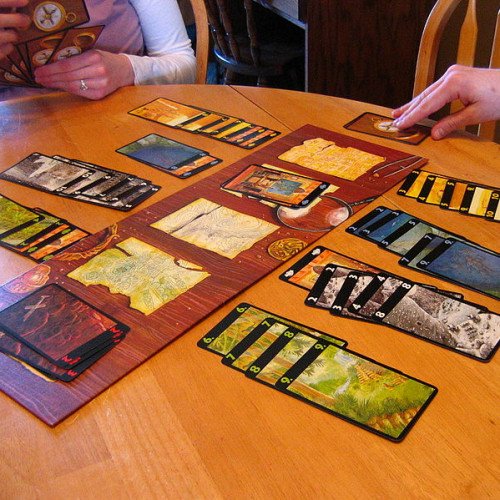

LOST CITIES
Lost Cities is a 60-card card game, designed in 1999 by game designer Reiner Knizia and published by several publishers. The objective of the game is to mount profitable expeditions to one or more of the five lost cities (the Himalayas, the Brazilian Rain Forest, the Desert Sands, the Ancient Volcanos and Neptune's Realm). The game was originally intended as a 2-player game, but rule variants have been contributed by fans to allow 1 or 2 further players, causing Reiner Knizia himself to later provide semi-official 4-player rules. Lost Cities is a fast-moving game, with players playing or discarding, and then replacing, a single card each turn. Cards represent progress on one of the five color-coded expeditions. Players must decide, during the course of the game, how many of these expeditions to actually embark upon. Card-play rules are quite straightforward, but because players can only move forward on an expedition (by playing cards which are higher-numbered than those already played), making the right choice in a given game situation can be quite difficult. An expedition that has been started will earn points according to how much progress has been made when the game ends, and after three rounds, the player with the highest total score wins the game. Each expedition that is started but not thoroughly charted incurs a negative point penalty (investment costs). Interaction between players is indirect, in that one cannot directly impact another player's expeditions. However, since players can draw from the common discard piles, they are free to make use of opposing discards. Additionally, since the available cards for a given expedition are finite, progress made by an opponent in a given color can lead to difficulty making progress in that same color. The game's board, while designed to supplement the theme, is optional and consists only of simple marked areas where players place discards. If Lost Cities had four expeditions instead of five, it could be played with a standard deck of playing cards. When doing so, the face cards would represent investment cards, with numbered cards two through ten serving as the expedition progress cards.
Statistics for this Xoptio
XIANGQI
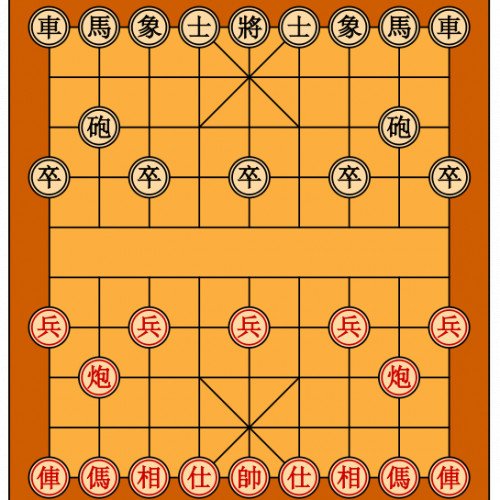
Xiangqi (Chinese: 象棋; pinyin: xiàngqí; Wade–Giles: Hsiang ch'i; English: /ˈʃɑːŋtʃi/), also called Chinese chess or Elephant chess, is a strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in China, and is in the same family as Western chess, chaturanga, shogi, Indian chess and janggi. Besides China and areas with significant ethnic Chinese communities, xiangqi is also a popular pastime in Vietnam, where it is known as cờ tướng. The game represents a battle between two armies, with the object of capturing the enemy's general (king). Distinctive features of xiangqi include the cannon (pao), which must jump to capture; a rule prohibiting the generals from facing each other directly; areas on the board called the river and palace, which restrict the movement of some pieces (but enhance that of others); and placement of the pieces on the intersections of the board lines, rather than within the squares. Xiangqi is played on a board nine lines wide and ten lines long. As in the game Go (圍碁; or Wei ch'i 圍棋), the pieces are placed on the intersections, which are known as points. The vertical lines are known as files (Chinese: 路; pinyin: lù; "road"), and the horizontal lines are known as ranks (Chinese: 線/綫; pinyin: xiàn; "line"). Centred at the first to third and eighth to tenth ranks of the board are two zones, each three points by three points, demarcated by two diagonal lines connecting opposite corners and intersecting at the centre point. Each of these areas is known as 宮 About this soundgōng, a castle. Dividing the two opposing sides, between the fifth and sixth ranks, is 河 hé, the "river". The river is often marked with the phrases 楚河 About this soundchǔ hé, meaning "River of the Chu ", and 漢界 About this soundhàn jiè, meaning "Border of the Han", a reference to the Chu–Han War. Although the river (or Hanchu boundary) provides a visual division between the two sides, only two pieces are affected by its presence: soldiers have an enhanced move after crossing the river, and elephants cannot cross it. The starting points of the soldiers and cannons are usually, but not always, marked with small crosses.