GAME OF THE GENERALS VS HEX

GAME OF THE GENERALS
The Game of the Generals, also called GG or GOG as it is most fondly called, or simply The Generals, is an educational war game invented in the Philippines by Sofronio H. Pasola Jr. in 1970. Its Filipino name is "Salpakan." It can be played within twenty to thirty minutes. It is designed for two players, each controlling an army, and a neutral arbiter (sometimes called a referee or an adjutant) to decide the results of "challenges" between opposing playing pieces, that like playing cards, have their identities hidden from the opponent. The game simulates armies at war trying to overpower, misinform, outflank, outmaneuver, and destroy each other. It optimizes the use of logic, memory, and spatial skills. It simulates the "fog of war" because the identities of the opposing pieces are hidden from each player and can only be guessed at by their location, movements, or from the results of challenges. The game allows only one side's plan to succeed, although a player may change plans during the course of the game. In addition, there are two different ways of winning the game (see below). Certain strategies and tactics, however, allow both sides the chance of securing a better idea of the other's plan as the game progresses. Players can also speak or gesture to their opponents during matches, hoping to create a false impression about the identity of their pieces or their overall strategy. This game was invented by Sofronio H. Pasola, Jr. with the inspiration of his son Ronnie Pasola. The Pasolas first tried the Game of the Generals on a chessboard. Even then, the pieces had no particular arrangement. There were no spies in the experimental game; but after Ronnie Pasola remembered the James Bond movies and Mata Hari, he added the Spies. Making the pieces hidden was the idea of the Pasolas after remembering card games. The Game of the Generals' public introduction was on February 28, 1973. After the game was made, it angered many Filipino chess players thinking that Pasola was trying to denigrate or supplant chess.
Statistics for this Xoptio
HEX
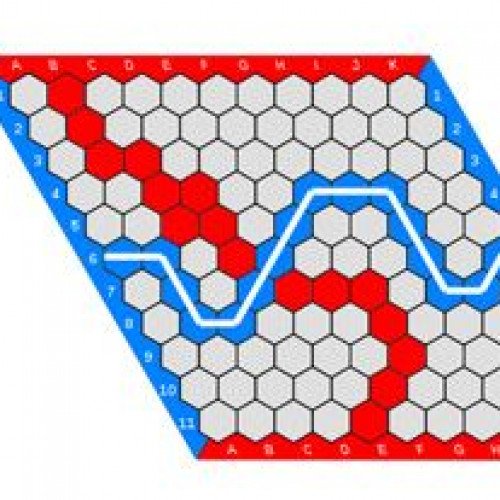
Hex is a two player abstract strategy board game in which players attempt to connect opposite sides of a hexagonal board. Hex was invented by mathematician and poet Piet Hein in 1942 and independently by John Nash in 1948. It is traditionally played on an 11×11 rhombus board, although 13×13 and 19×19 boards are also popular. Each player is assigned a pair of opposite sides of the board which they must try to connect by taking turns placing a stone of their color onto any empty space. Once placed, the stones are unable to be moved or removed. A player wins when they successfully connect their sides together through a chain of adjacent stones. Draws are impossible in Hex due to the topology of the game board. The game has deep strategy, sharp tactics and a profound mathematical underpinning related to the Brouwer fixed-point theorem. The game was first marketed as a board game in Denmark under the name Con-tac-tix, and Parker Brothers marketed a version of it in 1952 called Hex; they are no longer in production. Hex can also be played with paper and pencil on hexagonally ruled graph paper. Hex-related research is current in the areas of topology, graph and matroid theory, combinatorics, game theory and artificial intelligence.