DICEBALL VS HEX

DICEBALL
Diceball! is a board game in which two players roll dice to simulate a baseball game, one representing the visiting team and the other the home team. Both players use the dice to throw the baseball from the mound to the plate and field the ball on defense. Diceball! was designed to mirror the statistical reality of baseball. A regular game of Diceball! without extra innings lasts about 45 minutes. The game was designed in 1979 on a pizza box by a 16-year old Daniel Girard from Rawdon, Québec, while the Montreal Expos were chasing the pennant in the National League. Girard brought his game to his high school, where he organized tournaments with other students. Given the popularity of the game in his school, Girard also brought his game to university where it also became popular. The interest created by the game was noticed by entrepreneur Louis Desjardins, who launched the game with Girard. To start the game, the visiting team puts a pawn (as a batter and eventually runner) in the batter's box, to get the pitcher's throws. The die replaces the ball. The pitcher rolls the die until either the batter is struck out, the batter is walked, or the ball is hit. If the ball is hit, the offensive team rolls a die to determine the number of dice to be used to hit the ball. The number of dice indicated are rolled and added up. Numbers from 1 to 36 show the location where the ball is hit and the ball is placed on the game board. If the ball is hit on a circle, the ball was hit in the air and an out is recorded. If the ball is hit on a number in a cloud, it is a ground ball and that the batter will have to try to reach a base before the defense throws to that base. If the ball is hit to a star-shaped zone, the runner starts to run around the bases while the defence recovers the ball on the star. If the stars are from 27 to 36 it is a home run and all runners score. Every batter who runs around the bases and reaches home plate before three outs scores a run. As soon as three outs are recorded, stranded runners are removed from the bases. The teams trade places: the defense becomes the offense.
Statistics for this Xoptio
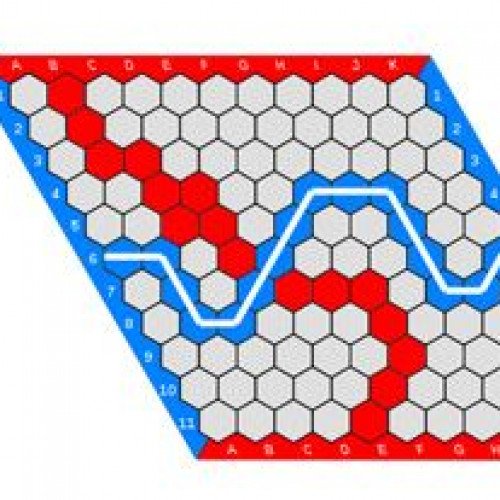
HEX
Hex is a two player abstract strategy board game in which players attempt to connect opposite sides of a hexagonal board. Hex was invented by mathematician and poet Piet Hein in 1942 and independently by John Nash in 1948. It is traditionally played on an 11×11 rhombus board, although 13×13 and 19×19 boards are also popular. Each player is assigned a pair of opposite sides of the board which they must try to connect by taking turns placing a stone of their color onto any empty space. Once placed, the stones are unable to be moved or removed. A player wins when they successfully connect their sides together through a chain of adjacent stones. Draws are impossible in Hex due to the topology of the game board. The game has deep strategy, sharp tactics and a profound mathematical underpinning related to the Brouwer fixed-point theorem. The game was first marketed as a board game in Denmark under the name Con-tac-tix, and Parker Brothers marketed a version of it in 1952 called Hex; they are no longer in production. Hex can also be played with paper and pencil on hexagonally ruled graph paper. Hex-related research is current in the areas of topology, graph and matroid theory, combinatorics, game theory and artificial intelligence.