DIAMOND VS SUGOROKU
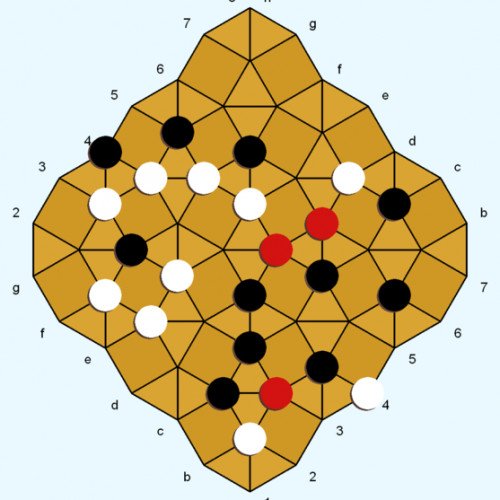
DIAMOND
Diamond is a two-player abstract strategy board game invented by Larry Back. The invention was inspired by the game Kensington, which uses a similar board pattern and game objective. Rules for Diamond were conceived in 1985 and finalized in 1994. Diamond introduces a new board geometry and neutral pieces, with the aim of enhancing the game dynamic and lowering the potential for draws. Diamond was featured in the February 2013 issue of Games magazine. The Diamond gameboard consists of interlocking squares and triangles. White and Black each control 12 game pieces of their own color. Neutral pieces (red-colored in the diagrams) enter the game via captures. The pieces are played on the line intersections (called points, as in Go). White and black (but not red) pieces can move along straight lines to adjacent unoccupied points. A player wins by being the first to occupy all four corners (points) of a board square with their pieces. Capturing moves are possible in the Movement phase. If the points of a triangle contain exactly one white and one black piece, either player can capture the opponent piece by occupying the remaining open point ("cornering" the enemy piece on the triangle). The captured piece can be cornered on one triangle (see Example 1), or simultaneously cornered on two different triangles (Example 4). The captured piece is immediately removed from the game and replaced on its point by a neutral piece. If a move simultaneously corners two opponent pieces on two different triangles, then neither enemy piece is captured (Examples 2 and 3). A piece can move safely to a triangle point even if the other two points of the triangle are occupied by enemy pieces (Example 5).
Statistics for this Xoptio

SUGOROKU
Sugoroku (雙六 or 双六) (literally 'double six') refers to two different forms of a Japanese board game: ban-sugoroku (盤双六, 'board-sugoroku') which is similar to western backgammon, and e-sugoroku (絵双六, 'picture-sugoroku') which is similar to western Snakes and Ladders. The game is thought to have been introduced from China (where it was known as Shuanglu) into Japan in the sixth century. It is known that in the centuries following the game's introduction into Japan it was made illegal several times, most prominently in 689 and 754. This is because the simple and luck-based nature of sugoroku made it an ideal gambling game. This version of sugoroku and records of playing for gambling continuously appeared until early Edo era. In early Edo-era, a new and quick gambling game called Chō-han (丁半) appeared and using sugoroku for gambling quickly dwindled. This variant of the backgammon family has died out in Japan and most other countries, with the Western style modern backgammon (with doubling-cube) having some avid players. A simpler e-sugoroku, with rules similar to snakes and ladders, appeared as early as late 13th century and was made popular due to the cheap and elaborate wooden block printing technology of the Edo period. Thousands of variations of boards were made with pictures and themes from religion, political, actors, and even adult material. In the Meiji and later periods, this variation of the game remained popular and was often included in child-oriented magazines. With ban-sugoroku being obsolete, today the word sugoroku almost always means e-sugoroku.