DIAMOND VS GAME OF THE GENERALS
DIAMOND
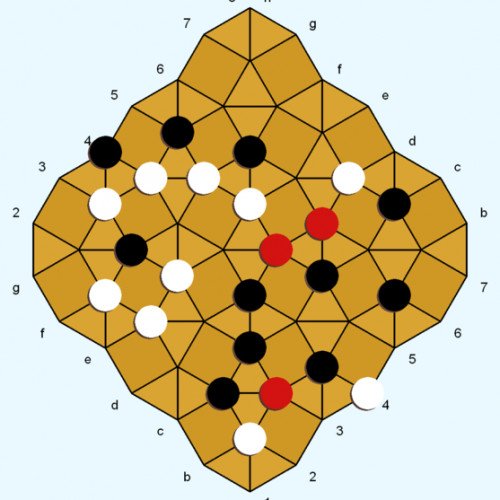
Diamond is a two-player abstract strategy board game invented by Larry Back. The invention was inspired by the game Kensington, which uses a similar board pattern and game objective. Rules for Diamond were conceived in 1985 and finalized in 1994. Diamond introduces a new board geometry and neutral pieces, with the aim of enhancing the game dynamic and lowering the potential for draws. Diamond was featured in the February 2013 issue of Games magazine. The Diamond gameboard consists of interlocking squares and triangles. White and Black each control 12 game pieces of their own color. Neutral pieces (red-colored in the diagrams) enter the game via captures. The pieces are played on the line intersections (called points, as in Go). White and black (but not red) pieces can move along straight lines to adjacent unoccupied points. A player wins by being the first to occupy all four corners (points) of a board square with their pieces. Capturing moves are possible in the Movement phase. If the points of a triangle contain exactly one white and one black piece, either player can capture the opponent piece by occupying the remaining open point ("cornering" the enemy piece on the triangle). The captured piece can be cornered on one triangle (see Example 1), or simultaneously cornered on two different triangles (Example 4). The captured piece is immediately removed from the game and replaced on its point by a neutral piece. If a move simultaneously corners two opponent pieces on two different triangles, then neither enemy piece is captured (Examples 2 and 3). A piece can move safely to a triangle point even if the other two points of the triangle are occupied by enemy pieces (Example 5).
Statistics for this Xoptio

GAME OF THE GENERALS
The Game of the Generals, also called GG or GOG as it is most fondly called, or simply The Generals, is an educational war game invented in the Philippines by Sofronio H. Pasola Jr. in 1970. Its Filipino name is "Salpakan." It can be played within twenty to thirty minutes. It is designed for two players, each controlling an army, and a neutral arbiter (sometimes called a referee or an adjutant) to decide the results of "challenges" between opposing playing pieces, that like playing cards, have their identities hidden from the opponent. The game simulates armies at war trying to overpower, misinform, outflank, outmaneuver, and destroy each other. It optimizes the use of logic, memory, and spatial skills. It simulates the "fog of war" because the identities of the opposing pieces are hidden from each player and can only be guessed at by their location, movements, or from the results of challenges. The game allows only one side's plan to succeed, although a player may change plans during the course of the game. In addition, there are two different ways of winning the game (see below). Certain strategies and tactics, however, allow both sides the chance of securing a better idea of the other's plan as the game progresses. Players can also speak or gesture to their opponents during matches, hoping to create a false impression about the identity of their pieces or their overall strategy. This game was invented by Sofronio H. Pasola, Jr. with the inspiration of his son Ronnie Pasola. The Pasolas first tried the Game of the Generals on a chessboard. Even then, the pieces had no particular arrangement. There were no spies in the experimental game; but after Ronnie Pasola remembered the James Bond movies and Mata Hari, he added the Spies. Making the pieces hidden was the idea of the Pasolas after remembering card games. The Game of the Generals' public introduction was on February 28, 1973. After the game was made, it angered many Filipino chess players thinking that Pasola was trying to denigrate or supplant chess.