CROSS AND CIRCLE GAME VS TAK
CROSS AND CIRCLE GAME
Cross and circle is a board game design used for race games played throughout the world. The basic design comprises a circle divided into four equal portions by a cross inscribed inside it like four spokes in a wheel; the classic example of this design is Yut. However, the term "cross and circle game" is also applied to boards that replace the circle with a square, and cruciform boards that collapse the circle onto the cross; all three types are topologically equivalent. Ludo and Parcheesi (both descendants of Pachisi) are examples of frequently played cruciform games. The category may also be expanded to include circular or square boards without a cross which are nevertheless quartered (Zohn Ahl), and boards that have more than four spokes (Aggravation, Trivial Pursuit). The game board for the Aztec game Patolli consists of a collapsed circle without an interior cross and thus has the distinction of being a cross that is a circle (topologically), without being a cross plus circle. Tokens are moved around spaces drawn on the circle and on the cross, with the goal of being the first player to move all tokens all the way around the board. Generally the circle of the cross and circle forms the primary circuit followed by the players' pieces. The function of the cross is more variable; for example, in Yut the cross forms shortcuts to the finish, whereas in Pachisi the four spokes are used as player-specific exits and entrances to the pieces' home. In non-race games (like Coppit and Trivial Pursuit) all paths may be undifferentiated in function.
Statistics for this Xoptio
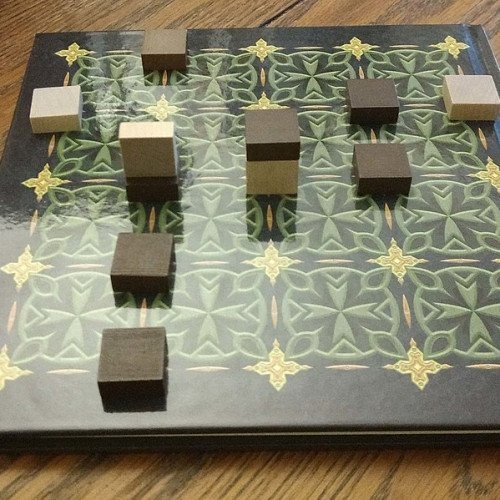

TAK
Tak is a two-player abstract strategy game designed by James Ernest and Patrick Rothfuss and published by Cheapass Games in 2016. The goal of Tak is to be the first to connect two opposite edges of the board with pieces called "stones", and create a road. To accomplish this, players take turns placing their own stones and building a road while blocking and capturing their opponent's stones to hinder their efforts at the same. A player "captures" a stone by stacking one of their pieces on top of the opponent's. These stacks can then be moved as a whole or broken up and moved across several spaces on the board. The vertical stacking and unstacking of stones gives a three dimensional element to the game play. A player may move a single piece or a stack of pieces they control. A stack is made when a player moves a stone on top of another flat stone of any color. The stone on top of a stack determines which player has control of that entire stack. All stones move orthogonally in a straight line on the board. There is no diagonal movement. A player can also move a whole stack in addition to single stones. A stack can be moved like a single stone, moved in its entirety one space orthogonally (North, South, East, or West), or it can move several spaces orthogonally by breaking the stack and placing one or more flat stones onto the squares being moved onto. The player can leave any number of stones, including zero, on the starting space, but must place at least one piece for each subsequent move. There is no height limit for stacks, but the amount of stones a player can remove from the stack and move is set by the "carry limit" of the board. The carry limit of the board is determined by the dimensions of the board. For example, if the stack was on a 5x5 board, the carry limit of the stack would be five. Because standing stones and capstones can't be stacked upon, there are no stacks with these pieces at the bottom or in the middle of the stack. Both of these stones however can be moved onto other flat stones to form a stack with them as the head. A capstone may "flatten" a standing stone and use it to form a stack with the capstone as its head, but it must do so alone. For example, a stack with a capstone cannot flatten a standing stone by moving as a stack onto the standing stone, but a stack can be used to move a capstone across the board so that the capstone alone moves to flatten the standing stone as the final movement.