CROSS AND CIRCLE GAME VS MAKRUK
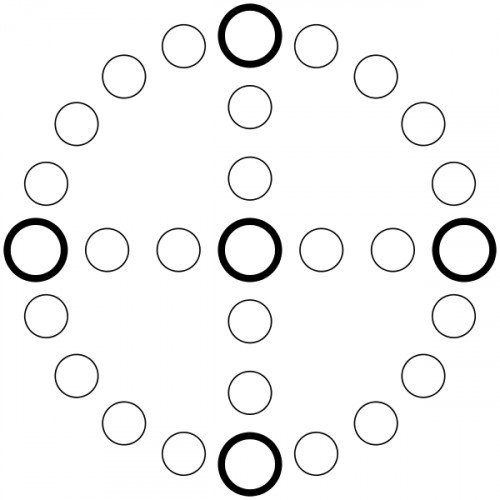
CROSS AND CIRCLE GAME
Cross and circle is a board game design used for race games played throughout the world. The basic design comprises a circle divided into four equal portions by a cross inscribed inside it like four spokes in a wheel; the classic example of this design is Yut. However, the term "cross and circle game" is also applied to boards that replace the circle with a square, and cruciform boards that collapse the circle onto the cross; all three types are topologically equivalent. Ludo and Parcheesi (both descendants of Pachisi) are examples of frequently played cruciform games. The category may also be expanded to include circular or square boards without a cross which are nevertheless quartered (Zohn Ahl), and boards that have more than four spokes (Aggravation, Trivial Pursuit). The game board for the Aztec game Patolli consists of a collapsed circle without an interior cross and thus has the distinction of being a cross that is a circle (topologically), without being a cross plus circle. Tokens are moved around spaces drawn on the circle and on the cross, with the goal of being the first player to move all tokens all the way around the board. Generally the circle of the cross and circle forms the primary circuit followed by the players' pieces. The function of the cross is more variable; for example, in Yut the cross forms shortcuts to the finish, whereas in Pachisi the four spokes are used as player-specific exits and entrances to the pieces' home. In non-race games (like Coppit and Trivial Pursuit) all paths may be undifferentiated in function.
Statistics for this Xoptio
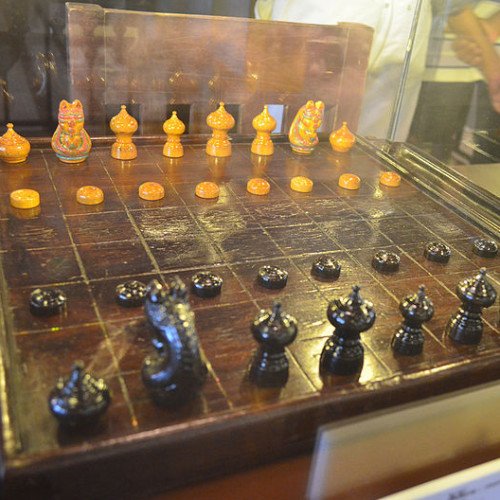

MAKRUK
Makruk or Thai chess, is a board game that is descended from the 6th-century Indian game of chaturanga or a close relative thereof, and is therefore related to chess. It is classified as a chess variant. The word "ruk" (Thai: รุก) in Thai is thought to derive from "rukh" which means "chariot" in the Persian language (and is also the common origin of the name for a rook in western chess). The Persian traders came to the Ayutthaya kingdom around the 14th century to spread their culture and to trade with the Thai kingdom. It is therefore possible that the Siamese Makruk, in its present form, was directly derived from the Persian game of Shatranj via the cultural exchange between the two people in this period. This is because the movement of Makruk Thai's queen, or the "seed" (Thai: เม็ด), is essentially the same as the ferz in Shatranj. The disadvantaged player announces the counting of his fleeing moves, starting from the number of pieces left on the board, including both kings. The winning player has to checkmate his opponent's king before the maximum number is announced, otherwise the game is declared a draw. During this process, the count may restart if the counting player would like to stop and start counting again. For example, if White has two rooks and a knight against a lone black king, he has three moves to checkmate his opponent (the given value of 8 minus the total number of pieces, 5). If Black captures a white rook, the count does not automatically restart, unless Black is willing to do so, at his own disadvantage. However, many players do not understand this and restart the counting while fleeing with the king.