CROSS AND CIRCLE GAME VS DALDØS
CROSS AND CIRCLE GAME
Cross and circle is a board game design used for race games played throughout the world. The basic design comprises a circle divided into four equal portions by a cross inscribed inside it like four spokes in a wheel; the classic example of this design is Yut. However, the term "cross and circle game" is also applied to boards that replace the circle with a square, and cruciform boards that collapse the circle onto the cross; all three types are topologically equivalent. Ludo and Parcheesi (both descendants of Pachisi) are examples of frequently played cruciform games. The category may also be expanded to include circular or square boards without a cross which are nevertheless quartered (Zohn Ahl), and boards that have more than four spokes (Aggravation, Trivial Pursuit). The game board for the Aztec game Patolli consists of a collapsed circle without an interior cross and thus has the distinction of being a cross that is a circle (topologically), without being a cross plus circle. Tokens are moved around spaces drawn on the circle and on the cross, with the goal of being the first player to move all tokens all the way around the board. Generally the circle of the cross and circle forms the primary circuit followed by the players' pieces. The function of the cross is more variable; for example, in Yut the cross forms shortcuts to the finish, whereas in Pachisi the four spokes are used as player-specific exits and entrances to the pieces' home. In non-race games (like Coppit and Trivial Pursuit) all paths may be undifferentiated in function.
Statistics for this Xoptio

DALDØS
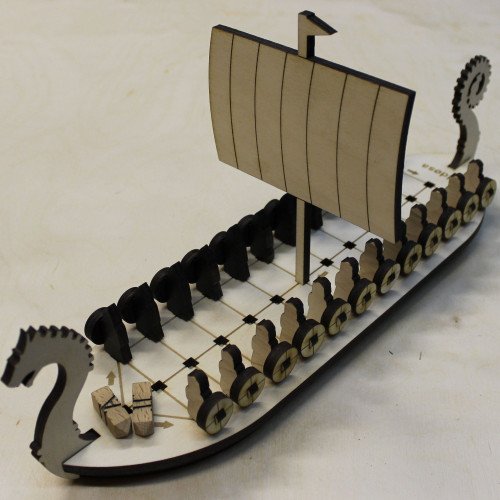
Daldøs is a running-fight board game only known from a few coastal locations in southern Scandinavia, where its history can be traced back to around 1800. The game is notable for its unusual four-sided dice (stick or long dice). In Denmark it is known as daldøs in Northern and Western Jutland (Mors, Thisted and Fanø), and possibly as daldos on Bornholm. In Norway it is known under the name of daldøsa from Jæren, where, unlike in Denmark, a continuous tradition of the daldøs game exists. Daldøs has much in common with some games in the sáhkku family of Sámi board games. Sáhkku is known to have been played among Sámi on the northern coast and eastern-central inland of Sápmi, far away from Jæren and Denmark. Otherwise, the closest relatives of this game appear to be the tâb games from Northern Africa and South-western Asia, possibly apart from one unlabelled diagram in a codex from Southern England. The board is boat-shaped and has three parallel rows of holes, two of which (A and B) have 16 holes each, while the middle row has an extra hole in the prow of the ship. Each player has 16 spatula-shaped pieces with a bottom end fitting into the holes of the board. One player has pieces that are rather wide and thin; whereas the other player's pieces are more obelisk-shaped. At the beginning of the game, player A's pieces are placed in the holes of row A so that the spatulas are perpendicular to the row (un-dalled), and equivalently for player B. Later in the game, the pieces will be turned (fordallede, or dalled) so that the spatula is parallel to the rows. Two special dice are used. Each die is a four-sided long die with pyramidal or rounded ends, preventing the die from standing on end. They may be about 2 by 2 cm in cross section, and 4 cm long. The four sides are marked A (with the value 1, called dallen, i.e. the dal), II (2, probably called døs), III (3) and IIII (4). According to some sources, the dal is opposite to III.