CHECKERS VS SITTUYIN
CHECKERS
Draughts (/drɑːfts, dræfts/; British English) or checkers (American English) is a group of strategy board games for two players which involve diagonal moves of uniform game pieces and mandatory captures by jumping over opponent pieces. Draughts developed from alquerque. The name 'draughts' derives from the verb to draw or to move, wheras 'checkers' derives from the checkered board which the game is played on. The most popular forms are English draughts, also called American checkers, played on an 8×8 checkerboard; Russian draughts, also played on an 8×8, and international draughts, played on a 10×10 board. There are many other variants played on 8×8 boards. Canadian checkers and Singaporean/Malaysian checkers (also locally known as dum) are played on a 12×12 board. English draughts was weakly solved in 2007 by a team of Canadian computer scientists led by Jonathan Schaeffer. From the standard starting position, both players can guarantee a draw with perfect play. Draughts is played by two opponents, on opposite sides of the gameboard. One player has the dark pieces; the other has the light pieces. Players alternate turns. A player may not move an opponent's piece. A move consists of moving a piece diagonally to an adjacent unoccupied square. If the adjacent square contains an opponent's piece, and the square immediately beyond it is vacant, the piece may be captured (and removed from the game) by jumping over it. Only the dark squares of the checkered board are used. A piece may move only diagonally into an unoccupied square. When presented, capturing is mandatory in most official rules, although some rule variations make capturing optional. In almost all variants, the player without pieces remaining, or who cannot move due to being blocked, loses the game.
Statistics for this Xoptio
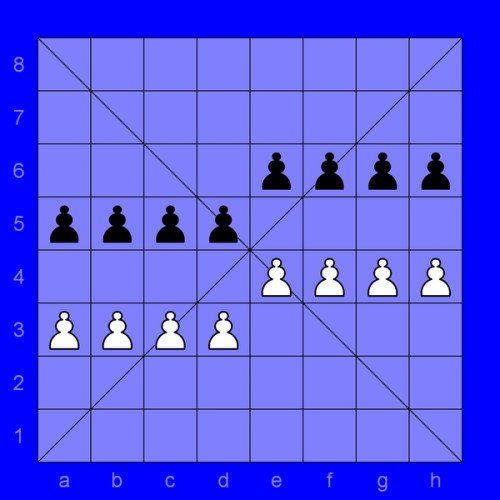
SITTUYIN
Sittuyin (Burmese: စစ်တုရင်), also known as Burmese chess, is a variant of chess that is a direct offspring of the Indian game of chaturanga which arrived in 8th century AD. Sit is the modern Burmese word for army or war ; the word sittuyin can be translated as representation of the four characteristics of army—chariot, elephant, cavalry and infantry. In its native land the game has been largely overshadowed by Western (international) chess, although it remains popular in the northwest regions. The sittuyin board consists of 64 squares, 8 rows and 8 columns, without alternating colors. It also consists of two diagonal lines across the board known as sit-ke-myin (general's lines). Only feudal lords (pawns) are on the board in the initial position. The game starts with the Red player (depicted here having white pieces), followed by the Black player, placing their other pieces arbitrarily on their own halves of the board (known as sit-tee or troops deployment): chariots can be put on any square on the back rank. In official tournaments, a small curtain is used on the middle of the board to prevent the players seeing each other's deployment during the sit-tee phase. One of the possible game openings is shown in the diagram. Feudal lords promote to general when they reach diagonal lines marked on the board. The promotion is possible only if that player's general has been captured. If the player has a feudal lord on a promotion square and his or her general is no longer on the board, the player can (if he or she wishes to) promote the feudal lord to general instead of making a move. A feudal lord which passes the promotion square cannot promote anymore.