CHECKERS VS SHATRANJ
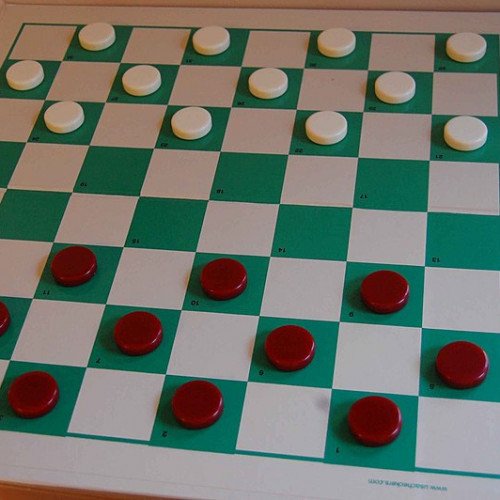
CHECKERS
Draughts (/drɑːfts, dræfts/; British English) or checkers (American English) is a group of strategy board games for two players which involve diagonal moves of uniform game pieces and mandatory captures by jumping over opponent pieces. Draughts developed from alquerque. The name 'draughts' derives from the verb to draw or to move, wheras 'checkers' derives from the checkered board which the game is played on. The most popular forms are English draughts, also called American checkers, played on an 8×8 checkerboard; Russian draughts, also played on an 8×8, and international draughts, played on a 10×10 board. There are many other variants played on 8×8 boards. Canadian checkers and Singaporean/Malaysian checkers (also locally known as dum) are played on a 12×12 board. English draughts was weakly solved in 2007 by a team of Canadian computer scientists led by Jonathan Schaeffer. From the standard starting position, both players can guarantee a draw with perfect play. Draughts is played by two opponents, on opposite sides of the gameboard. One player has the dark pieces; the other has the light pieces. Players alternate turns. A player may not move an opponent's piece. A move consists of moving a piece diagonally to an adjacent unoccupied square. If the adjacent square contains an opponent's piece, and the square immediately beyond it is vacant, the piece may be captured (and removed from the game) by jumping over it. Only the dark squares of the checkered board are used. A piece may move only diagonally into an unoccupied square. When presented, capturing is mandatory in most official rules, although some rule variations make capturing optional. In almost all variants, the player without pieces remaining, or who cannot move due to being blocked, loses the game.
Statistics for this Xoptio

SHATRANJ
Shatranj (Arabic: شطرنج; Persian: شترنج; from Middle Persian chatrang چترنگ) is an old form of chess, as played in the Sasanian Empire. Its origins are in the Indian game of chaturaṅga. Modern chess gradually developed from this game, as it was introduced to the western world by contacts in Muslim Al-Andalus (modern Spain) and in Sicily in the 10th century. The Persian word shatranj ultimately derives from Sanskrit (Sanskrit: चतुरङ्ग; caturaṅga) (catuḥ: "four"; anga: "arm"), referring to the game of the same name: Chaturanga. In Middle Persian the word appears as chatrang, with the 'u' lost due to syncope and the 'a' lost to apocope, such as in the title of the text Mâdayân î chatrang ("Book of Chess") from the 7th century AD. In Persian folk etymology, a Persian text refers to Shah Ardashir I, who ruled from 224–241, as a master of the game: Three books written in Pahlavi, Kar-Namag i Ardashir i Pabagan, Khosrow and ridag, and Wizārišn ī čhatrang ("Treatise on Chess"), also known as the Chatrang Nama ("Book of Chess"), all mention chatrang. In Kār-nāmak it is said that Ardashīr "with the help of the gods became more victorious and experienced than all others in polo, horsemanship, chess, backgammon, and other arts," and in the small treatise on Khosrow and ridag, the latter declares that he is superior to his comrades in chess, backgammon, and hašt pāy. Bozorgmehr, the author of Wizārišn ī čhatrang, describes how the game of chess was sent as a test to Khosrow I (r. 531-79) by the "king of the Hindus Dēvsarm" with the envoy Takhtarītūs and how the test was answered by the vizier Bozorgmehr, who in his turn invented the game Backgammon as a test for the Hindus. These three Middle Persian sources do not give any certain indication of the date when chess was introduced into Persia. The mentions of chess in Kar-Namag i Ardashir i Pabagan and Khosrow and ridag are simply conventional and may easily represent late Sasanian or even post-Sasanian redactions. According to Touraj Daryaee, Kar-Namag i Ardashir i Pabagan is from 6th century. Wizārišn ī čhatrang was written in the 6th century.