CHECKERS VS SENET
CHECKERS
Draughts (/drɑːfts, dræfts/; British English) or checkers (American English) is a group of strategy board games for two players which involve diagonal moves of uniform game pieces and mandatory captures by jumping over opponent pieces. Draughts developed from alquerque. The name 'draughts' derives from the verb to draw or to move, wheras 'checkers' derives from the checkered board which the game is played on. The most popular forms are English draughts, also called American checkers, played on an 8×8 checkerboard; Russian draughts, also played on an 8×8, and international draughts, played on a 10×10 board. There are many other variants played on 8×8 boards. Canadian checkers and Singaporean/Malaysian checkers (also locally known as dum) are played on a 12×12 board. English draughts was weakly solved in 2007 by a team of Canadian computer scientists led by Jonathan Schaeffer. From the standard starting position, both players can guarantee a draw with perfect play. Draughts is played by two opponents, on opposite sides of the gameboard. One player has the dark pieces; the other has the light pieces. Players alternate turns. A player may not move an opponent's piece. A move consists of moving a piece diagonally to an adjacent unoccupied square. If the adjacent square contains an opponent's piece, and the square immediately beyond it is vacant, the piece may be captured (and removed from the game) by jumping over it. Only the dark squares of the checkered board are used. A piece may move only diagonally into an unoccupied square. When presented, capturing is mandatory in most official rules, although some rule variations make capturing optional. In almost all variants, the player without pieces remaining, or who cannot move due to being blocked, loses the game.
Statistics for this Xoptio
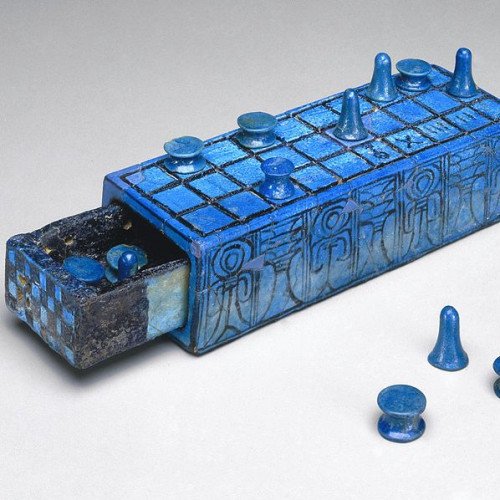

SENET
Senet is a board game from ancient Egypt. The earliest representation of senet is dated to c. 2620 BCE from the Mastaba of Hesy-Re, while similar boards and hieroglyphic signs are found even earlier. The game fell out of use following the Roman periodand its original rules are the subject of conjecture. Senet is the oldest known board game. Fragmentary boards that could be senet have been found in First Dynasty burials in Egypt, c. 3100 BCE. The first unequivocal painting of this ancient game is from the Third Dynasty tomb of Hesy (c. 2686–2613 BCE). People are depicted playing senet in a painting in the tomb of Rashepes, as well as from other tombs of the Fifth and Sixth Dynasties (c. 2500 BCE). The oldest intact senet boards date to the Middle Kingdom, but graffiti on Fifth and Sixth Dynasty monuments could date as early as the Old Kingdom. At least by the time of the New Kingdom in Egypt (1550–1077 BCE), senet was conceived as a representation of the journey of the ka (the vital spark) to the afterlife. This connection is made in the Great Game Text, which appears in a number of papyri, as well as the appearance of markings of religious significance on senet boards themselves. The game is also referred to in chapter XVII of the Book of the Dead. A study on a senet board in the Rosicrucian Egyptian Museum, dating back to the early New Kingdom of Egypt, showed the evolution of the game from its secular origins into a more religious artifact. Senet also was played by people in neighboring cultures, and it probably came to those places through trade relationships between Egyptians and local peoples. It has been found in the Levant at sites such as Arad and Byblos, as well as in Cyprus. Because of the local practice of making games out of stone, there are more senet games that have been found in Cyprus than have been found in Egypt.