CHECKERS VS FANORONA
CHECKERS
Draughts (/drɑːfts, dræfts/; British English) or checkers (American English) is a group of strategy board games for two players which involve diagonal moves of uniform game pieces and mandatory captures by jumping over opponent pieces. Draughts developed from alquerque. The name 'draughts' derives from the verb to draw or to move, wheras 'checkers' derives from the checkered board which the game is played on. The most popular forms are English draughts, also called American checkers, played on an 8×8 checkerboard; Russian draughts, also played on an 8×8, and international draughts, played on a 10×10 board. There are many other variants played on 8×8 boards. Canadian checkers and Singaporean/Malaysian checkers (also locally known as dum) are played on a 12×12 board. English draughts was weakly solved in 2007 by a team of Canadian computer scientists led by Jonathan Schaeffer. From the standard starting position, both players can guarantee a draw with perfect play. Draughts is played by two opponents, on opposite sides of the gameboard. One player has the dark pieces; the other has the light pieces. Players alternate turns. A player may not move an opponent's piece. A move consists of moving a piece diagonally to an adjacent unoccupied square. If the adjacent square contains an opponent's piece, and the square immediately beyond it is vacant, the piece may be captured (and removed from the game) by jumping over it. Only the dark squares of the checkered board are used. A piece may move only diagonally into an unoccupied square. When presented, capturing is mandatory in most official rules, although some rule variations make capturing optional. In almost all variants, the player without pieces remaining, or who cannot move due to being blocked, loses the game.
Statistics for this Xoptio
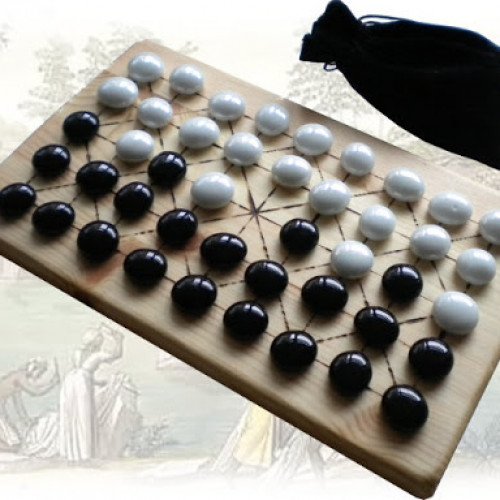

FANORONA
Fanorona (Malagasy pronunciation: [fə̥ˈnurnə̥]) is a strategy board game for two players. The game is indigenous to Madagascar. Fanorona has three standard versions: Fanoron-Telo, Fanoron-Dimy, and Fanoron-Tsivy. The difference between these variants is the size of board played on. Fanoron-Telo is played on a 3×3 board and the difficulty of this game can be compared to the game of tic-tac-toe. Fanoron-Dimy is played on a 5×5 board and Fanoron-Tsivy is played on a 9×5 board—Tsivy being the most popular. The Tsivy board consists of lines and intersections that create a grid with 5 rows and 9 columns subdivided diagonally to form part of the tetrakis square tiling of the plane. A line represents the path along which a stone can move during the game. There are weak and strong intersections. At a weak intersection it is only possible to move a stone horizontally and vertically, while on a strong intersection it is also possible to move a stone diagonally. A stone can only move from one intersection to an adjacent intersection. Black and white pieces, twenty-two each, are arranged on all points but the center. The objective of the game is to capture all the opponents pieces. The game is a draw if neither player succeeds in this. Fanorona is very popular in Madagascar. According to one version of a popular legend, an astrologer had advised King Ralambo to choose his successor by selecting a time when his sons were away from the capital to feign sickness and urge their return; his kingdom would be given to the first son who returned home to him. When the king's messenger reached Ralambo's elder son Prince Andriantompokondrindra, he was playing fanorona and trying to win a telo noho dimy (3 against 5) situation, one that is infamously difficult to resolve. As a result, his younger brother Prince Andrianjaka was the first to arrive and inherited the throne.