CHATURANGA VS SITTUYIN

CHATURANGA
Chaturanga (Sanskrit: चतुरङ्ग; caturaṅga), or catur for short, which means 'Four Divisions' (referring to ancient army divisions of infantry Pawn (chess), cavalry Knight (chess), elephantry Alfil (chess), and chariotry Rook (chess)), is an ancient Indian strategy game that is commonly theorized to be the common ancestor of the board games chess, xiangqi, shogi, sittuyin, and makruk. Chaturanga is first known from the Gupta Empire in India around the 6th century AD. In the 7th century, it was adopted as chatrang (shatranj) in Sassanid Persia, which in turn was the form of chess brought to late-medieval Europe. According to Stewart Culin, chaturanga was first described in the Hindu text Bhavishya Purana. The exact rules of chaturanga are unknown. Chess historians suppose that the game had similar rules to those of its successor, shatranj. In particular, there is uncertainty as to the moves of the Gaja (elephant). The origin of chaturanga has been a puzzle for centuries. It has its origins in the Gupta Empire, with the earliest clear reference dating from the sixth century of the common era, and from north India. The first substantial argument that chaturanga is much older than this is the fact that the chariot is the most powerful piece on the board, although chariots appear to have been obsolete in warfare for at least five or six centuries. The counter-argument is that they remained prominent in literature. Several more recent scholars have proposed a gradual evolution in the centuries B.C. in the northern or northwestern border areas of Indian culture, where it was in contact with Greek culture brought by the Macedonian-Greek army, and where some rulers issued coins with fused Greek-Indian imagery. Myron Samsin argues that chaturanga originated in the kingdom of Bactria, ca. 255–55 B.C., in a fusion of the many short-moving men of the Greek game petteia, or poleis, with men derived from the various moves of an Indian race game, perhaps Seega or Chaupur, on the ashtapada, the board of another race game.
Statistics for this Xoptio
SITTUYIN
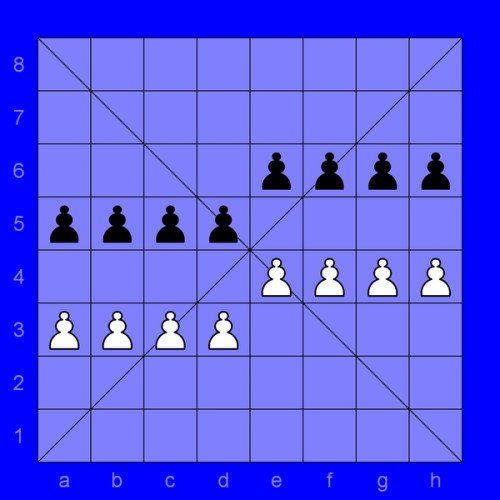
Sittuyin (Burmese: စစ်တုရင်), also known as Burmese chess, is a variant of chess that is a direct offspring of the Indian game of chaturanga which arrived in 8th century AD. Sit is the modern Burmese word for army or war ; the word sittuyin can be translated as representation of the four characteristics of army—chariot, elephant, cavalry and infantry. In its native land the game has been largely overshadowed by Western (international) chess, although it remains popular in the northwest regions. The sittuyin board consists of 64 squares, 8 rows and 8 columns, without alternating colors. It also consists of two diagonal lines across the board known as sit-ke-myin (general's lines). Only feudal lords (pawns) are on the board in the initial position. The game starts with the Red player (depicted here having white pieces), followed by the Black player, placing their other pieces arbitrarily on their own halves of the board (known as sit-tee or troops deployment): chariots can be put on any square on the back rank. In official tournaments, a small curtain is used on the middle of the board to prevent the players seeing each other's deployment during the sit-tee phase. One of the possible game openings is shown in the diagram. Feudal lords promote to general when they reach diagonal lines marked on the board. The promotion is possible only if that player's general has been captured. If the player has a feudal lord on a promotion square and his or her general is no longer on the board, the player can (if he or she wishes to) promote the feudal lord to general instead of making a move. A feudal lord which passes the promotion square cannot promote anymore.