CHATURANGA VS GIPF

CHATURANGA
Chaturanga (Sanskrit: चतुरङ्ग; caturaṅga), or catur for short, which means 'Four Divisions' (referring to ancient army divisions of infantry Pawn (chess), cavalry Knight (chess), elephantry Alfil (chess), and chariotry Rook (chess)), is an ancient Indian strategy game that is commonly theorized to be the common ancestor of the board games chess, xiangqi, shogi, sittuyin, and makruk. Chaturanga is first known from the Gupta Empire in India around the 6th century AD. In the 7th century, it was adopted as chatrang (shatranj) in Sassanid Persia, which in turn was the form of chess brought to late-medieval Europe. According to Stewart Culin, chaturanga was first described in the Hindu text Bhavishya Purana. The exact rules of chaturanga are unknown. Chess historians suppose that the game had similar rules to those of its successor, shatranj. In particular, there is uncertainty as to the moves of the Gaja (elephant). The origin of chaturanga has been a puzzle for centuries. It has its origins in the Gupta Empire, with the earliest clear reference dating from the sixth century of the common era, and from north India. The first substantial argument that chaturanga is much older than this is the fact that the chariot is the most powerful piece on the board, although chariots appear to have been obsolete in warfare for at least five or six centuries. The counter-argument is that they remained prominent in literature. Several more recent scholars have proposed a gradual evolution in the centuries B.C. in the northern or northwestern border areas of Indian culture, where it was in contact with Greek culture brought by the Macedonian-Greek army, and where some rulers issued coins with fused Greek-Indian imagery. Myron Samsin argues that chaturanga originated in the kingdom of Bactria, ca. 255–55 B.C., in a fusion of the many short-moving men of the Greek game petteia, or poleis, with men derived from the various moves of an Indian race game, perhaps Seega or Chaupur, on the ashtapada, the board of another race game.
Statistics for this Xoptio
GIPF
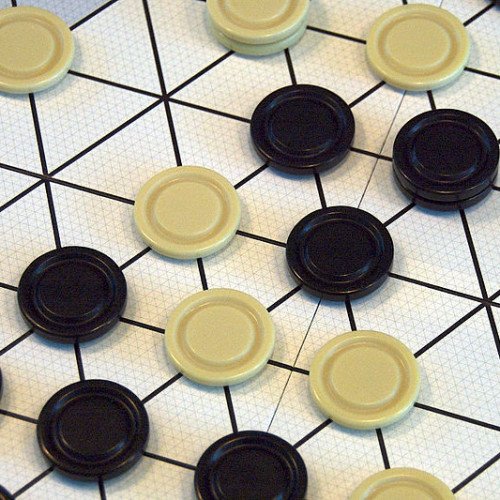
GIPF is an abstract strategy board game by Kris Burm, the first of six games in his series of games called the GIPF Project. GIPF was recommended by Spiel des Jahres in 1998. Players take turns pushing tokens (one player taking black, the other white) from the edge of the tri-gridded, hexagonal board, with pieces already in play pushed in front of the new placements rather than allowing more than one piece on any space. The game is lost if a player has no more tokens to play, and since each starts with a set number of tokens, it is clearly necessary to recycle pieces already positioned to keep playing. This is achieved by contriving to line up four pieces of the same colour in a row on the board, at which point those tokens are returned to their owner, and any opposing tokens extending from the line of four are captured. Because a single player will often move several pieces and change numerous on-board relationships, it is remarkably difficult to predict the state of the board more than one turn ahead, despite GIPF being a game of perfect information. Play tends to be highly fluid and there is no real concept of long term territorial or spatial development. The game can be expanded with extra pieces (available separately) called Potentials, which allow different kinds of moves to be made. These are named for the other games in the GIPF Project, though the other games are not actually necessary in order to utilise the Potentials named after them.