CAMELOT VS SHOGI
CAMELOT
Camelot is a strategy board game for two players. It was invented by George S. Parker late in the 19th century, and was one of the first games published by Parker Brothers, originally under the name Chivalry. The game was reissued as "Camelot" in 1930, with reduced size and number of pieces. It flourished through numerous editions and variants, achieving its greatest popularity in the 1930s, and remained in print through the late 1960s. Parker Brothers briefly republished the game in the 1980s under the name Inside Moves. Since then it has been out of print, but retains a core of fans anticipating another revival. Camelot is easy to learn and without extensive theory or praxis, making it perhaps more accessible for novices to play/enjoy compared to chess. Gameplay is exceptionally tactical almost from the first move, so games are quick to play to a finish. A World Camelot Federation exists, with free membership, led by Michael W. Nolan. Camelot was featured in Abstract Games magazine in 2001 and 2002. In 1882, George S. Parker began working on an abstract board game called Chivalry. His goal was to create a game not so difficult as chess, but considerably more varied than checkers. Parker created a game that was a complex, tactical, but an easily learned and quickly played mixture of Halma and checkers. When finally published by Geo. S. Parker & Co. in 1887, Chivalry won the raves of chess and checkers experts, but the game Parker called "the best game in 2000 years" did not catch on quickly with the general public. However, Parker never lost his enthusiasm for the game, and in 1930 he made a few changes, and Parker Brothers republished it under the name "Camelot". A few more rules changes followed in 1931. Camelot enjoyed its greatest popularity in the 1930s. Camelot players included José Raúl Capablanca, World Chess Champion from 1921 to 1927, and Frank Marshall, U.S. Chess Champion from 1907 to 1936. Sidney Lenz and Milton Work, two world-famous bridge players, also played the game. There were over 50 different editions of Camelot sets issued, including a gold-stamped leather edition and a mahogany cabinet edition. There were tournament editions, regular editions, and low-cost editions. Camelot was eventually discontinued in 1968, then reissued as "Inside Moves" in 1985, and finally discontinued again in 1986.
Statistics for this Xoptio

SHOGI
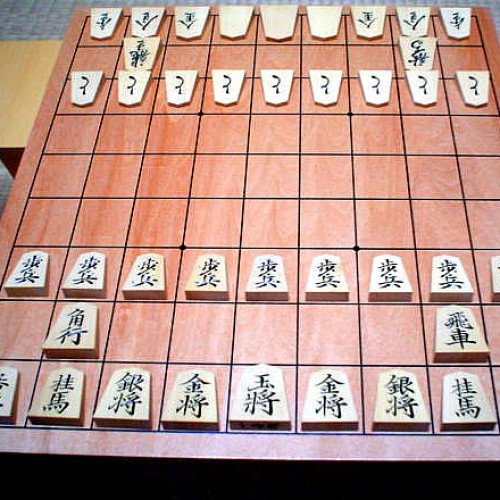
Shogi (将棋, shōgi, English: /ˈʃoʊɡiː/, Japanese: , also known as Japanese chess or the Game of Generals, is a two-player strategy board game that is the Japanese variant of chess. It is the most popular chess variant in Japan. Shōgi means general's (shō 将) board game (gi 棋). Shogi was the earliest chess variant to allow captured pieces to be returned to the board by the capturing player. This drop rule is speculated to have been invented in the 15th century and possibly connected to the practice of 15th century mercenaries switching loyalties when captured instead of being killed. The earliest predecessor of the game, chaturanga, originated in India in the 6th century, and the game was likely transmitted to Japan via China or Korea sometime after the Nara period. Shogi in its present form was played as early as the 16th century, while a direct ancestor without the drop rule was recorded from 1210 in a historical document Nichūreki, which is an edited copy of Shōchūreki and Kaichūreki from the late Heian period (c. 1120). Two players face each other across a board composed of rectangles in a grid of 9 ranks (rows, 段) by 9 files (columns, 筋) yielding an 81 square board. In Japanese they are called Sente 先手 (first player) and Gote 後手 (second player), but in English are conventionally referred to as Black and White, with Black the first player. The board is nearly always rectangular, and the rectangles are undifferentiated by marking or color. Pairs of dots mark the players' promotion zones.