CAMELOT VS LOST CITIES
CAMELOT
Camelot is a strategy board game for two players. It was invented by George S. Parker late in the 19th century, and was one of the first games published by Parker Brothers, originally under the name Chivalry. The game was reissued as "Camelot" in 1930, with reduced size and number of pieces. It flourished through numerous editions and variants, achieving its greatest popularity in the 1930s, and remained in print through the late 1960s. Parker Brothers briefly republished the game in the 1980s under the name Inside Moves. Since then it has been out of print, but retains a core of fans anticipating another revival. Camelot is easy to learn and without extensive theory or praxis, making it perhaps more accessible for novices to play/enjoy compared to chess. Gameplay is exceptionally tactical almost from the first move, so games are quick to play to a finish. A World Camelot Federation exists, with free membership, led by Michael W. Nolan. Camelot was featured in Abstract Games magazine in 2001 and 2002. In 1882, George S. Parker began working on an abstract board game called Chivalry. His goal was to create a game not so difficult as chess, but considerably more varied than checkers. Parker created a game that was a complex, tactical, but an easily learned and quickly played mixture of Halma and checkers. When finally published by Geo. S. Parker & Co. in 1887, Chivalry won the raves of chess and checkers experts, but the game Parker called "the best game in 2000 years" did not catch on quickly with the general public. However, Parker never lost his enthusiasm for the game, and in 1930 he made a few changes, and Parker Brothers republished it under the name "Camelot". A few more rules changes followed in 1931. Camelot enjoyed its greatest popularity in the 1930s. Camelot players included José Raúl Capablanca, World Chess Champion from 1921 to 1927, and Frank Marshall, U.S. Chess Champion from 1907 to 1936. Sidney Lenz and Milton Work, two world-famous bridge players, also played the game. There were over 50 different editions of Camelot sets issued, including a gold-stamped leather edition and a mahogany cabinet edition. There were tournament editions, regular editions, and low-cost editions. Camelot was eventually discontinued in 1968, then reissued as "Inside Moves" in 1985, and finally discontinued again in 1986.
Statistics for this Xoptio

LOST CITIES
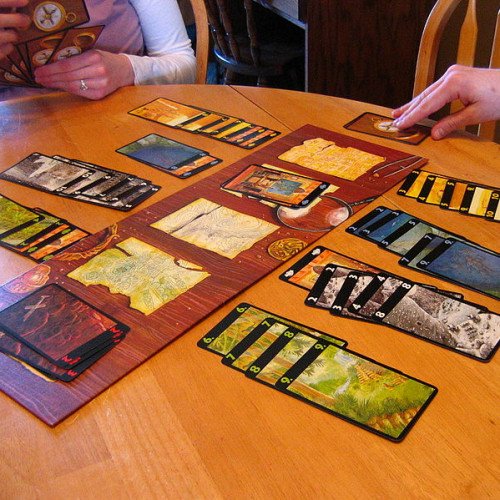
Lost Cities is a 60-card card game, designed in 1999 by game designer Reiner Knizia and published by several publishers. The objective of the game is to mount profitable expeditions to one or more of the five lost cities (the Himalayas, the Brazilian Rain Forest, the Desert Sands, the Ancient Volcanos and Neptune's Realm). The game was originally intended as a 2-player game, but rule variants have been contributed by fans to allow 1 or 2 further players, causing Reiner Knizia himself to later provide semi-official 4-player rules. Lost Cities is a fast-moving game, with players playing or discarding, and then replacing, a single card each turn. Cards represent progress on one of the five color-coded expeditions. Players must decide, during the course of the game, how many of these expeditions to actually embark upon. Card-play rules are quite straightforward, but because players can only move forward on an expedition (by playing cards which are higher-numbered than those already played), making the right choice in a given game situation can be quite difficult. An expedition that has been started will earn points according to how much progress has been made when the game ends, and after three rounds, the player with the highest total score wins the game. Each expedition that is started but not thoroughly charted incurs a negative point penalty (investment costs). Interaction between players is indirect, in that one cannot directly impact another player's expeditions. However, since players can draw from the common discard piles, they are free to make use of opposing discards. Additionally, since the available cards for a given expedition are finite, progress made by an opponent in a given color can lead to difficulty making progress in that same color. The game's board, while designed to supplement the theme, is optional and consists only of simple marked areas where players place discards. If Lost Cities had four expeditions instead of five, it could be played with a standard deck of playing cards. When doing so, the face cards would represent investment cards, with numbered cards two through ten serving as the expedition progress cards.