BUL VS SITTUYIN
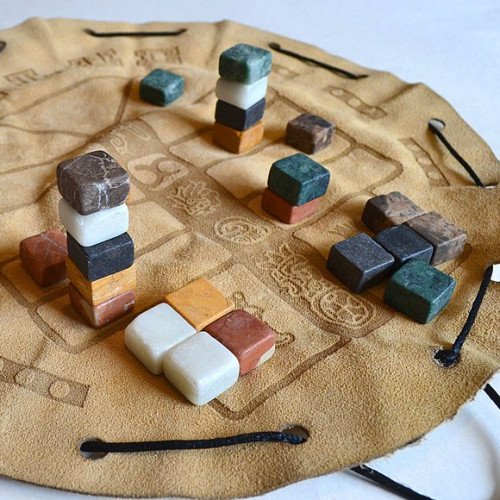

BUL
Bul (also called Buul, Boolik or Puluc) is a running-fight board game originating in Mesoamerica, and is known particularly among several of the Maya peoples of Belize and the Guatemalan highlands. It is uncertain whether this game dates back to the pre-Columbian Maya civilization, or whether it developed in the post-colonial era after the arrival of the Spanish conquistadores. Stewart Culin described the game in the 24th Annual Report of the Bureau of American Ethnology: Games of North American Indians published in 1907. R. C. Bell referred to the game in Board and Table Games from Many Civilizations. Both of these descriptions were based on the eyewitness accounts of others. Lieve Verbeeck, a linguist studying Mayan language, witnessed the modern version of the game being played by Mopan and Kekchi Maya in Belize It is not known exactly when the game was developed or what the original rules were as very few records survived the invasion by the conquistadors between the 15th and 17th centuries. Stewart Culin organised the games in his anthology into those he thought had an influence from Europe in their creation. Bul is not listed among these, and in his opinion the game must have developed before Europeans arrived in Central America. There are a variety of ways to play the game, as Verbeeck's account shows. The game could be played by two people, or by two equal-sized teams. The overall objective is to capture and subsequently kill the playing pieces of the opposition, so the game is in essence a war game. The playing area is divided into equal spaces using rods placed parallel to each other. The two players have control of a base at either end of the play area. The players take an even number of stones or figurines (or any suitable playing piece) and place them in their respective bases.
Statistics for this Xoptio
SITTUYIN
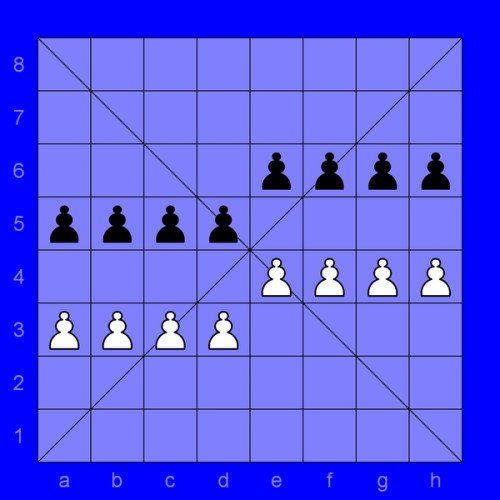
Sittuyin (Burmese: စစ်တုရင်), also known as Burmese chess, is a variant of chess that is a direct offspring of the Indian game of chaturanga which arrived in 8th century AD. Sit is the modern Burmese word for army or war ; the word sittuyin can be translated as representation of the four characteristics of army—chariot, elephant, cavalry and infantry. In its native land the game has been largely overshadowed by Western (international) chess, although it remains popular in the northwest regions. The sittuyin board consists of 64 squares, 8 rows and 8 columns, without alternating colors. It also consists of two diagonal lines across the board known as sit-ke-myin (general's lines). Only feudal lords (pawns) are on the board in the initial position. The game starts with the Red player (depicted here having white pieces), followed by the Black player, placing their other pieces arbitrarily on their own halves of the board (known as sit-tee or troops deployment): chariots can be put on any square on the back rank. In official tournaments, a small curtain is used on the middle of the board to prevent the players seeing each other's deployment during the sit-tee phase. One of the possible game openings is shown in the diagram. Feudal lords promote to general when they reach diagonal lines marked on the board. The promotion is possible only if that player's general has been captured. If the player has a feudal lord on a promotion square and his or her general is no longer on the board, the player can (if he or she wishes to) promote the feudal lord to general instead of making a move. A feudal lord which passes the promotion square cannot promote anymore.