BUL VS HARE AND HOUNDS
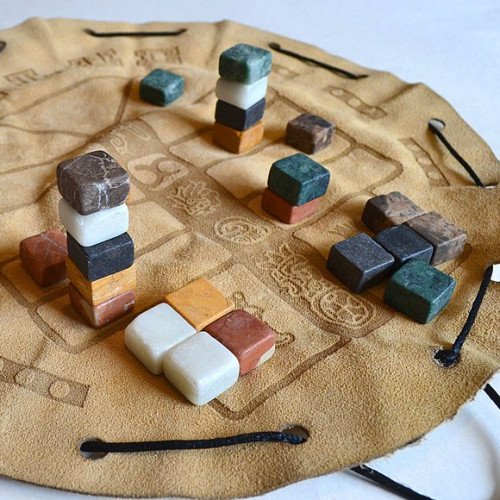

BUL
Bul (also called Buul, Boolik or Puluc) is a running-fight board game originating in Mesoamerica, and is known particularly among several of the Maya peoples of Belize and the Guatemalan highlands. It is uncertain whether this game dates back to the pre-Columbian Maya civilization, or whether it developed in the post-colonial era after the arrival of the Spanish conquistadores. Stewart Culin described the game in the 24th Annual Report of the Bureau of American Ethnology: Games of North American Indians published in 1907. R. C. Bell referred to the game in Board and Table Games from Many Civilizations. Both of these descriptions were based on the eyewitness accounts of others. Lieve Verbeeck, a linguist studying Mayan language, witnessed the modern version of the game being played by Mopan and Kekchi Maya in Belize It is not known exactly when the game was developed or what the original rules were as very few records survived the invasion by the conquistadors between the 15th and 17th centuries. Stewart Culin organised the games in his anthology into those he thought had an influence from Europe in their creation. Bul is not listed among these, and in his opinion the game must have developed before Europeans arrived in Central America. There are a variety of ways to play the game, as Verbeeck's account shows. The game could be played by two people, or by two equal-sized teams. The overall objective is to capture and subsequently kill the playing pieces of the opposition, so the game is in essence a war game. The playing area is divided into equal spaces using rods placed parallel to each other. The two players have control of a base at either end of the play area. The players take an even number of stones or figurines (or any suitable playing piece) and place them in their respective bases.
Statistics for this Xoptio
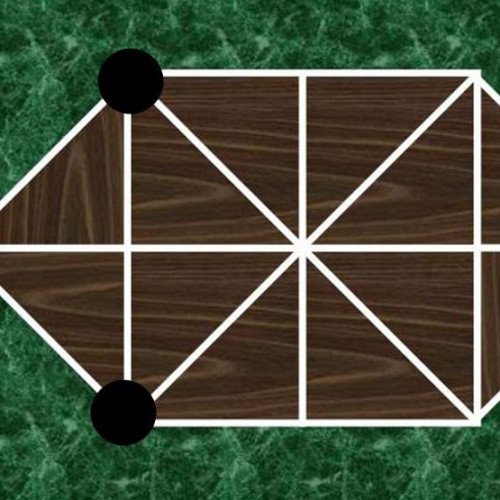
HARE AND HOUNDS
Hare games are two-player abstract strategy board games that were popular in medieval northern Europe up until the 19th century. In this game, a hare is trying to get past three dogs who are trying to surround it and trap it. The three dogs are represented by three pieces which normally start on one end of the board, and the hare is represented by one piece that usually starts in the middle of the board or is dropped on any vacant point in the beginning of the game. Hare games are similar to Bear games and hunt games. One side has more pieces than the other with the larger side attempting to hem in the smaller side. The smaller side though is usually compensated with more powers. Where Hare games differ is that the hounds can only move forward or sideways, and not backwards. The hunters in the Bear games can move in all directions. Furthermore, the dog in the Hare games cannot capture any of the hares, unlike the tigers, leopards, jaguars, and foxes in the hunt games which can capture their respective prey counterparts. There are several different Hare game boards depending upon the country of origin. Many preferred the narrow double-ended spearhead-like boards with orthogonal and diagonal lines running through them. There were several variations on this design. However, one in Denmark used a round board, and another design is found in Latvia. Hare games are referred to by different names. In 19th century France, a hare game that was popular among the military was called The Soldiers' Game. The dog is sometimes referred to as a hound, and hence the alternative title to this game as Hare and hounds. Other names are French Military Game, Game of Dwarfs, The Devil among tailors, and Trevolpa or Volpalejden . As the rules of the game are simple to program, there are many electronic implementations of the game. The second link below allows you to play this game. In this computer game, the hares and hounds are reversed. Instead, it is the hounds attempting to surround and immobilize the hare.