BLOCKADE VS GIPF
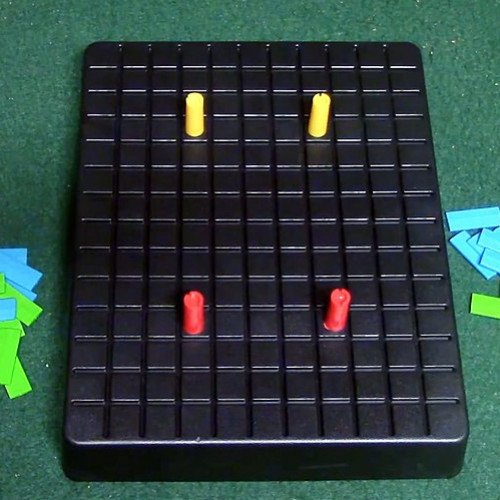

BLOCKADE
Blockade (also known as Cul-de-sac) is a strategy board game for two players with the motto "beat the barrier". It's played on a board with an 11x14 grid of spaces, barriers and 2 mobile playing pieces per player. The object of the game is to maneuver ones pieces around barriers and into the opponents starting spaces. The game is long out of production. Blockade was created by Philip Slater in 1975. In United States, it was published by Lakeside under the name Blockade. In France, Germany, Sweden, and United Kingdom the game was published by Lazy Days under the name Cul-de-sac (French, translation dead-end). The rules are simple, but it provides an interesting and deep game. Each player are given 2 pawns, 9 green walls (placed vertically), and 9 blue walls (placed horizontally). Pawns are placed on their starting locations on each of the four corners of the 11×14 board. First players' starting location is at [4,4] and [8,4], and the second players' is at [4,11] and [8,11]. The object of the game is for each player to get both their pawns to the starting locations of their opponent. The first to do so wins. On each turn, a player moves one pawn one or two spaces (horizontally, vertically, or any combination of the two) and places one wall anywhere on the board (useful for blocking off their opponent's move). Walls always cover two squares and must be placed according to their color (vertically or horizontally). Pawns may jump over other pawns that are blocking their path. Once players are out of walls, they keep moving pawns until one wins.
Statistics for this Xoptio
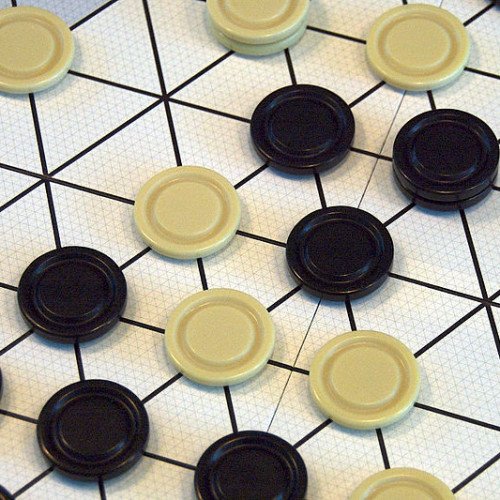
GIPF
GIPF is an abstract strategy board game by Kris Burm, the first of six games in his series of games called the GIPF Project. GIPF was recommended by Spiel des Jahres in 1998. Players take turns pushing tokens (one player taking black, the other white) from the edge of the tri-gridded, hexagonal board, with pieces already in play pushed in front of the new placements rather than allowing more than one piece on any space. The game is lost if a player has no more tokens to play, and since each starts with a set number of tokens, it is clearly necessary to recycle pieces already positioned to keep playing. This is achieved by contriving to line up four pieces of the same colour in a row on the board, at which point those tokens are returned to their owner, and any opposing tokens extending from the line of four are captured. Because a single player will often move several pieces and change numerous on-board relationships, it is remarkably difficult to predict the state of the board more than one turn ahead, despite GIPF being a game of perfect information. Play tends to be highly fluid and there is no real concept of long term territorial or spatial development. The game can be expanded with extra pieces (available separately) called Potentials, which allow different kinds of moves to be made. These are named for the other games in the GIPF Project, though the other games are not actually necessary in order to utilise the Potentials named after them.