AGON VS SUGOROKU
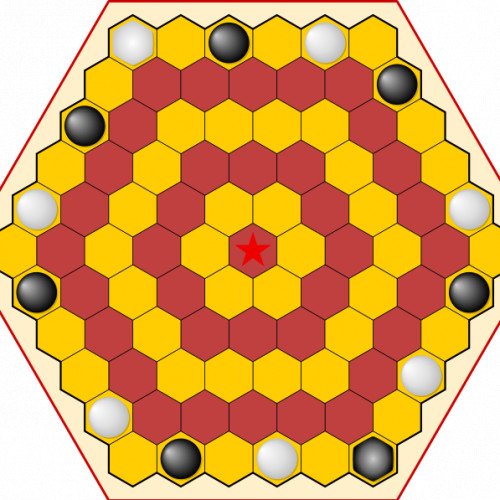
AGON
Agon (or Queen's Guards or Royal Guards) is an strategy game invented by Anthony Peacock of London, and first published in 1842. It is a two player game played on a 6×6×6 hexagonal gameboard, and is notable for being the oldest known board game played on a board of hexagonal cells. Each player has one queen and six guards. Players determine who moves first, then turns alternate. On each turn, a player moves one of his pieces. The object of the game is to be first to maneuver one's queen to the central hex (the throne) at the center of the board, and surround her with all six of her guards. The gameboard may be thought of as a series of concentric rings of hex cells (highlighted by rings of alternating colors). Pieces move one step at a time to an adjacent cell, either sideways in the same ring, or towards the throne to the next ring. The cell moved to must be vacant. Only the queen may move to the throne.
Statistics for this Xoptio

SUGOROKU
Sugoroku (雙六 or 双六) (literally 'double six') refers to two different forms of a Japanese board game: ban-sugoroku (盤双六, 'board-sugoroku') which is similar to western backgammon, and e-sugoroku (絵双六, 'picture-sugoroku') which is similar to western Snakes and Ladders. The game is thought to have been introduced from China (where it was known as Shuanglu) into Japan in the sixth century. It is known that in the centuries following the game's introduction into Japan it was made illegal several times, most prominently in 689 and 754. This is because the simple and luck-based nature of sugoroku made it an ideal gambling game. This version of sugoroku and records of playing for gambling continuously appeared until early Edo era. In early Edo-era, a new and quick gambling game called Chō-han (丁半) appeared and using sugoroku for gambling quickly dwindled. This variant of the backgammon family has died out in Japan and most other countries, with the Western style modern backgammon (with doubling-cube) having some avid players. A simpler e-sugoroku, with rules similar to snakes and ladders, appeared as early as late 13th century and was made popular due to the cheap and elaborate wooden block printing technology of the Edo period. Thousands of variations of boards were made with pictures and themes from religion, political, actors, and even adult material. In the Meiji and later periods, this variation of the game remained popular and was often included in child-oriented magazines. With ban-sugoroku being obsolete, today the word sugoroku almost always means e-sugoroku.