AGON VS DIAMOND
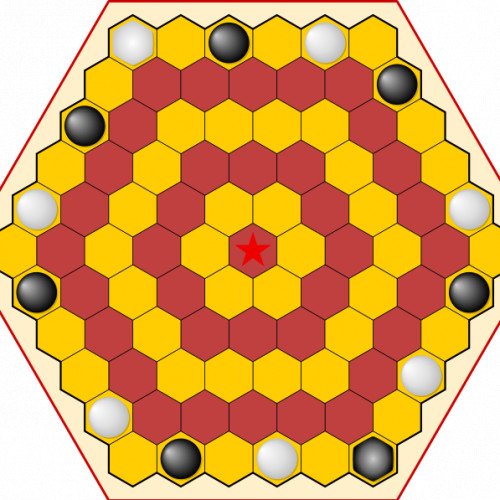
AGON
Agon (or Queen's Guards or Royal Guards) is an strategy game invented by Anthony Peacock of London, and first published in 1842. It is a two player game played on a 6×6×6 hexagonal gameboard, and is notable for being the oldest known board game played on a board of hexagonal cells. Each player has one queen and six guards. Players determine who moves first, then turns alternate. On each turn, a player moves one of his pieces. The object of the game is to be first to maneuver one's queen to the central hex (the throne) at the center of the board, and surround her with all six of her guards. The gameboard may be thought of as a series of concentric rings of hex cells (highlighted by rings of alternating colors). Pieces move one step at a time to an adjacent cell, either sideways in the same ring, or towards the throne to the next ring. The cell moved to must be vacant. Only the queen may move to the throne.
Statistics for this Xoptio
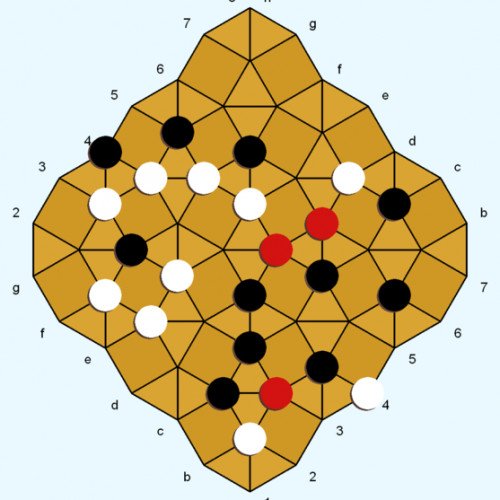
DIAMOND
Diamond is a two-player abstract strategy board game invented by Larry Back. The invention was inspired by the game Kensington, which uses a similar board pattern and game objective. Rules for Diamond were conceived in 1985 and finalized in 1994. Diamond introduces a new board geometry and neutral pieces, with the aim of enhancing the game dynamic and lowering the potential for draws. Diamond was featured in the February 2013 issue of Games magazine. The Diamond gameboard consists of interlocking squares and triangles. White and Black each control 12 game pieces of their own color. Neutral pieces (red-colored in the diagrams) enter the game via captures. The pieces are played on the line intersections (called points, as in Go). White and black (but not red) pieces can move along straight lines to adjacent unoccupied points. A player wins by being the first to occupy all four corners (points) of a board square with their pieces. Capturing moves are possible in the Movement phase. If the points of a triangle contain exactly one white and one black piece, either player can capture the opponent piece by occupying the remaining open point ("cornering" the enemy piece on the triangle). The captured piece can be cornered on one triangle (see Example 1), or simultaneously cornered on two different triangles (Example 4). The captured piece is immediately removed from the game and replaced on its point by a neutral piece. If a move simultaneously corners two opponent pieces on two different triangles, then neither enemy piece is captured (Examples 2 and 3). A piece can move safely to a triangle point even if the other two points of the triangle are occupied by enemy pieces (Example 5).