ABALONE VS XIANGQI
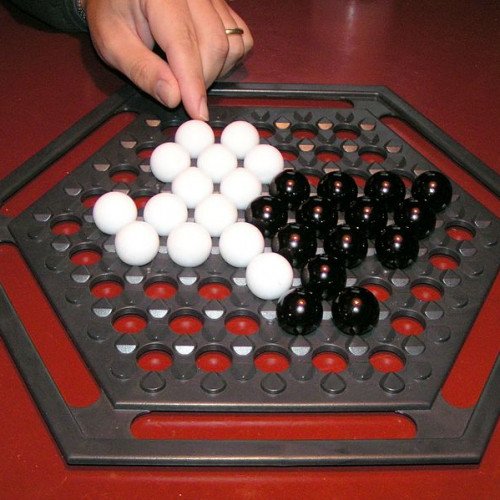

ABALONE
Abalone is a two-player abstract strategy board game designed by Michel Lalet and Laurent Lévi in 1987. Players are represented by opposing black and white marbles on a hexagonal board with the objective of pushing six of the opponent's marbles off the edge of the board. Abalone was published in 1990 and has sold more than 4.5 million units. The year it was published it received one of the first Mensa Select awards. It is currently sold in more than thirty countries. The board consists of 61 circular spaces arranged in a hexagon, five on a side. Each player has 14 marbles that rest in the spaces and are initially arranged as shown below, on the left image. The players take turns with the black marbles moving first. For each move, a player moves a straight line of one, two or three marbles of one color one space in one of six directions. The move can be either broadside / arrow-like (parallel to the line of marbles) or in-line / in a line (serial in respect to the line of marbles), as illustrated below. A player can push their opponent's marbles (a "sumito") that are in a line to their own with an in-line move only. They can only push if the pushing line has more marbles than the pushed line (three can push one or two; two can push one). Marbles must be pushed to an empty space (i.e. not blocked by a marble) or off the board. The winner is the first player to push six of the opponent's marbles off of the edge of the board.
Statistics for this Xoptio
XIANGQI
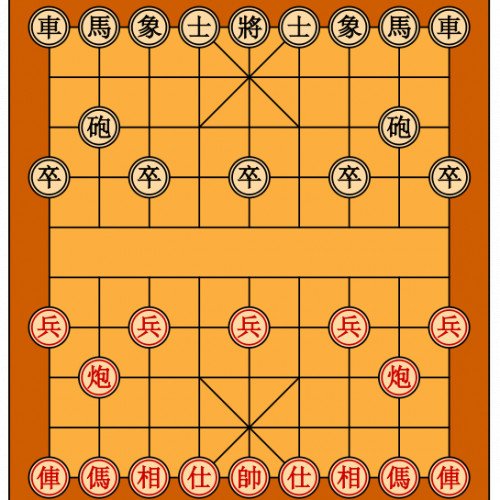
Xiangqi (Chinese: 象棋; pinyin: xiàngqí; Wade–Giles: Hsiang ch'i; English: /ˈʃɑːŋtʃi/), also called Chinese chess or Elephant chess, is a strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in China, and is in the same family as Western chess, chaturanga, shogi, Indian chess and janggi. Besides China and areas with significant ethnic Chinese communities, xiangqi is also a popular pastime in Vietnam, where it is known as cờ tướng. The game represents a battle between two armies, with the object of capturing the enemy's general (king). Distinctive features of xiangqi include the cannon (pao), which must jump to capture; a rule prohibiting the generals from facing each other directly; areas on the board called the river and palace, which restrict the movement of some pieces (but enhance that of others); and placement of the pieces on the intersections of the board lines, rather than within the squares. Xiangqi is played on a board nine lines wide and ten lines long. As in the game Go (圍碁; or Wei ch'i 圍棋), the pieces are placed on the intersections, which are known as points. The vertical lines are known as files (Chinese: 路; pinyin: lù; "road"), and the horizontal lines are known as ranks (Chinese: 線/綫; pinyin: xiàn; "line"). Centred at the first to third and eighth to tenth ranks of the board are two zones, each three points by three points, demarcated by two diagonal lines connecting opposite corners and intersecting at the centre point. Each of these areas is known as 宮 About this soundgōng, a castle. Dividing the two opposing sides, between the fifth and sixth ranks, is 河 hé, the "river". The river is often marked with the phrases 楚河 About this soundchǔ hé, meaning "River of the Chu ", and 漢界 About this soundhàn jiè, meaning "Border of the Han", a reference to the Chu–Han War. Although the river (or Hanchu boundary) provides a visual division between the two sides, only two pieces are affected by its presence: soldiers have an enhanced move after crossing the river, and elephants cannot cross it. The starting points of the soldiers and cannons are usually, but not always, marked with small crosses.