A GAME OF WAR VS HARE AND HOUNDS

A GAME OF WAR
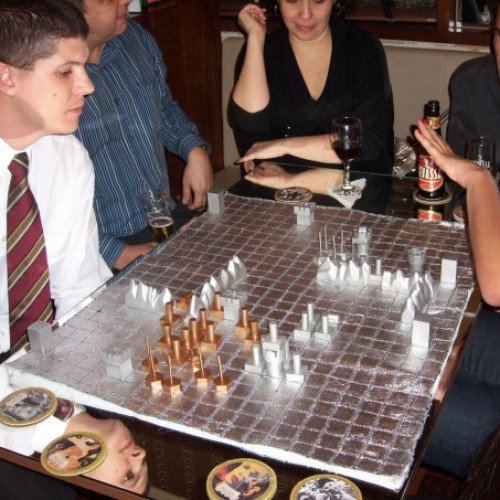
A Game of War is a book by Guy Debord and Alice Becker-Ho that illustrates a game devised by Debord by giving a detailed account of one of their table-top conflicts. It was first published in French as Le Jeu de la Guerre in 1987, but unsold copies were later pulped in 1991, along with other books by Debord, at his insistence when he left his publisher Champ libre. The book was reissued in 2006, with an English translation published by Atlas Press in 2008. In his 1989 book Panegyric, Guy Debord remarked: So I have studied the logic of war. Indeed I succeeded long ago in representing its essential movements on a rather simple game-board… I played this game, and in the often difficult conduct of my life drew a few lessons from it — setting rules for my life, and abiding by them. The surprises vouchsafed by this Kriegspiel of mine seem endless; I rather fear it may turn out to be the only one of my works to which people will venture to accord any value. As to whether I have made good use of its lessons, I shall leave that for others to judge. Apart from the books which contain the game, free online versions of the game are available. London based group, Class Wargames have reproduced A Game of War and taken it on a campaign around the globe, at Belo Horizonte, pictured above, St. Petersburg and a variety of other locations.
Statistics for this Xoptio
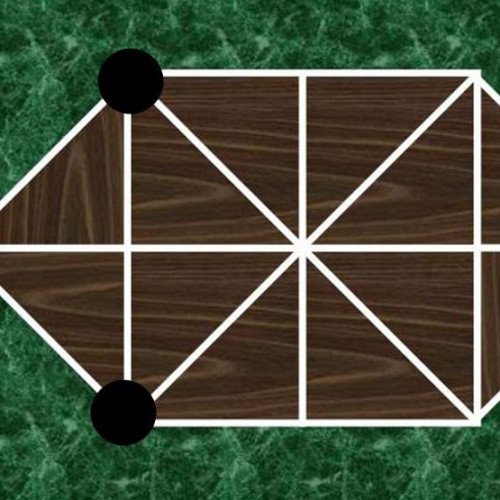
HARE AND HOUNDS
Hare games are two-player abstract strategy board games that were popular in medieval northern Europe up until the 19th century. In this game, a hare is trying to get past three dogs who are trying to surround it and trap it. The three dogs are represented by three pieces which normally start on one end of the board, and the hare is represented by one piece that usually starts in the middle of the board or is dropped on any vacant point in the beginning of the game. Hare games are similar to Bear games and hunt games. One side has more pieces than the other with the larger side attempting to hem in the smaller side. The smaller side though is usually compensated with more powers. Where Hare games differ is that the hounds can only move forward or sideways, and not backwards. The hunters in the Bear games can move in all directions. Furthermore, the dog in the Hare games cannot capture any of the hares, unlike the tigers, leopards, jaguars, and foxes in the hunt games which can capture their respective prey counterparts. There are several different Hare game boards depending upon the country of origin. Many preferred the narrow double-ended spearhead-like boards with orthogonal and diagonal lines running through them. There were several variations on this design. However, one in Denmark used a round board, and another design is found in Latvia. Hare games are referred to by different names. In 19th century France, a hare game that was popular among the military was called The Soldiers' Game. The dog is sometimes referred to as a hound, and hence the alternative title to this game as Hare and hounds. Other names are French Military Game, Game of Dwarfs, The Devil among tailors, and Trevolpa or Volpalejden . As the rules of the game are simple to program, there are many electronic implementations of the game. The second link below allows you to play this game. In this computer game, the hares and hounds are reversed. Instead, it is the hounds attempting to surround and immobilize the hare.