Phoenix (mythology) VS Apep
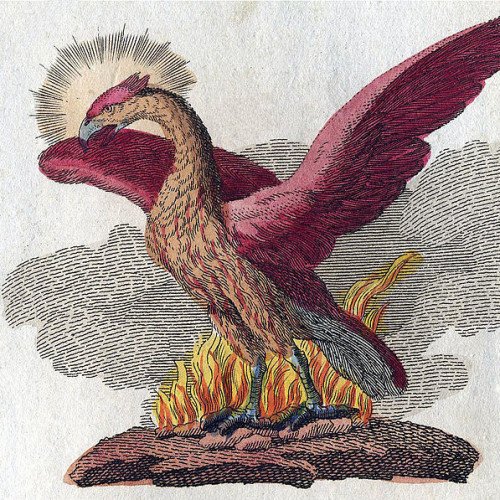
Phoenix (mythology)
In Ancient Greek folklore, a phoenix (; Ancient Greek: φοῖνιξ, phoînix) is a long-lived bird that cyclically regenerates or is otherwise born again. Associated with the sun, a phoenix obtains new life by arising from the ashes of its predecessor. Some legends say it dies in a show of flames and combustion, others that it simply dies and decomposes before being born again.Over time the phoenix motif spread from its origins in classical folklore and gained a variety of new associations: Herodotus, Lucan, Pliny the Elder, Pope Clement I, Lactantius, Ovid, and Isidore of Seville are among those who have contributed to the retelling and transmission of the phoenix motif. Over time, extending beyond its origins in classical Greek folklore, the phoenix could variously "symbolize renewal in general as well as the sun, time, the Empire, metempsychosis, consecration, resurrection, life in the heavenly Paradise, Christ, Mary, virginity, the exceptional man, and certain aspects of Christian life". In the Motif-Index of Folk-Literature, a tool used by folklorists, the phoenix is classified as motif B32.
Statistics for this Xoptio

Apep
Apep ( or ; also spelled Apepi or Aapep) or Apophis (; Ancient Greek: Ἄποφις) was the ancient Egyptian deity who embodied chaos (ı͗zft in Egyptian) and was thus the opponent of light and Ma'at (order/truth). He appears in art as a giant serpent. His name is reconstructed by Egyptologists as *ʻAʼpāp(ī), as it was written ꜥꜣpp(y) and survived in later Coptic as Ⲁⲫⲱⲫ Aphōph. Apep was first mentioned in the Eighth Dynasty, and he was honored in the names of the Fourteenth Dynasty king 'Apepi and of the Greater Hyksos king Apophis.