Vote on Mythical creatures: Phoenix (mythology) vs Piasa
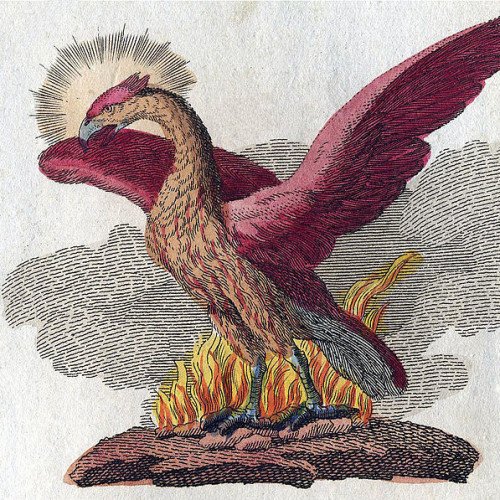
Phoenix (mythology)
In Ancient Greek folklore, a phoenix (; Ancient Greek: φοῖνιξ, phoînix) is a long-lived bird that cyclically regenerates or is otherwise born again. Associated with the sun, a phoenix obtains new life by arising from the ashes of its predecessor. Some legends say it dies in a show of flames and combustion, others that it simply dies and decomposes before being born again.Over time the phoenix motif spread from its origins in classical folklore and gained a variety of new associations: Herodotus, Lucan, Pliny the Elder, Pope Clement I, Lactantius, Ovid, and Isidore of Seville are among those who have contributed to the retelling and transmission of the phoenix motif. Over time, extending beyond its origins in classical Greek folklore, the phoenix could variously "symbolize renewal in general as well as the sun, time, the Empire, metempsychosis, consecration, resurrection, life in the heavenly Paradise, Christ, Mary, virginity, the exceptional man, and certain aspects of Christian life". In the Motif-Index of Folk-Literature, a tool used by folklorists, the phoenix is classified as motif B32.
Statistics for this Xoptio
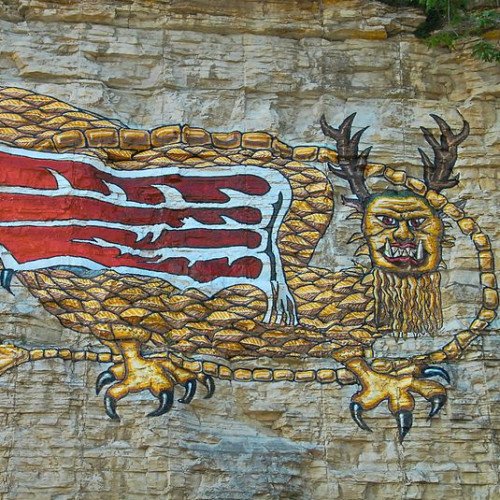

Piasa
The Piasa (/ˈpaɪ.əsɔː/ PY-ə-saw) or Piasa Bird is a Native American dragon depicted in one of two murals painted by Native Americans on bluffs (cliffsides) above the Mississippi River. Its original location was at the end of a chain of limestone bluffs in Madison County, Illinois at present-day Alton, Illinois. The original Piasa illustration no longer exists; a newer 20th-century version, based partly on 19th-century sketches and lithographs, has been placed on a bluff in Alton, Illinois, several hundred yards upstream from its origin. The location of the present-day mural is at 38.898055, -90.19915. The limestone rock quality on the new site is unsuited for holding an image, and the painting must be regularly restored. The original site of the painting was a high-quality (6–8 foot thick) layer of lithographic limestone, which was predominantly quarried away in the late 1870s by the Mississippi Lime Company.